Tumor immune microenvironment delineates progression trajectories of distinct nasopharyngeal carcinoma phenotypes
- PMID: 40412382
- PMCID: PMC12208333
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102143
Tumor immune microenvironment delineates progression trajectories of distinct nasopharyngeal carcinoma phenotypes
Abstract
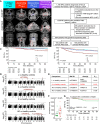
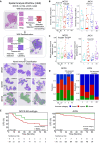
We investigate the molecular landscape of locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (LA-NPC) subtypes: limited (L), ascending (A), descending (D), and ascending-descending (AD). Using a cohort of 994 patients, we perform germline and somatic whole-exome sequencing (WES), transcriptomic profiling, multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC), and spatial histopathological analyses of tumor whole-slide images (WSIs). Germline WES reveals the most variants in AD subtypes, but somatic WES shows no subtype-specific mutations. Transcriptomics reveals higher extracellular matrix (ECM) gene expression in A and AD subtypes and higher immune gene expression in D and AD subtypes, agreeing with deconvolution and mIHC. Tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) of node-negative (N0) and node-positive (N+) L subtypes, considered early nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), resembles A and D subtypes, respectively, suggesting distinct evolutionary trajectories. Spatial WSI analyses identify the most immune-dense tumors among D subtypes and association of TIME with disease-free survival in AD subtypes. These findings highlight the TIME's role in LA-NPC progression and its potential impact on treatment strategies.
Keywords: ascending; descending; genomics; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; tumor immune microenvironment.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests M.L.K.C. reports personal fees from Astellas, Pfizer, MSD, AstraZeneca, Varian, Janssen, IQVIA, and Telix Pharmaceuticals; non-financial support from AstraZeneca; non-financial support from Veracyte Inc; grants from Ferring; personal fees and grants from Bayer; and personal fees and grants from BeiGene and consults for immunoSCAPE Inc. M.L.K.C. is a co-inventor of the patent of a High Sensitivity Lateral Flow Immunoassay For Detection of Analyte in Sample (10202107837T), Singapore, and serves on the Board of Directors of Digital Life Line Pte Ltd that owns the licensing agreement of the patent, outside the submitted work. L.-H.L. and J.-Y.J.L. are co-founders and shareholders of ImmunoQs Pte. Ltd. L.-H.L. and J.-Y.J.L. performed the multiplex image analyses as staff of ImmunoQs Pte. Ltd. and wrote and reviewed the image analysis methods as staff of BII, A∗STAR, who originally developed the methods.
Figures





References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Laversanne M., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M., Znaor A., Soerjomataram I., Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; 2024. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today.https://gco.iarc.fr/en
-
- Chen Y.-P., Ismaila N., Chua M.L.K., Colevas A.D., Haddad R., Huang S.H., Wee J.T.S., Whitley A.C., Yi J.-L., Yom S.S., et al. Chemotherapy in Combination With Radiotherapy for Definitive-Intent Treatment of Stage II-IVA Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: CSCO and ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39:840–859. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03237. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yao J.-J., Qi Z.-Y., Liu Z.-G., Jiang G.-M., Xu X.-W., Chen S.-Y., Zhu F.-T., Zhang W.-J., Lawrence W.R., Ma J., et al. Clinical features and survival outcomes between ascending and descending types of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era: A big-data intelligence platform-based analysis. Radiother. Oncol. 2019;137:137–144. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.04.025. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

