Lower baseline amyloid beta burden is associated with greater percent of amyloid beta positron emission tomography reduction and better clinical outcomes in the aducanumab Phase 3 trials ENGAGE and EMERGE in early Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 40413110
- PMCID: PMC12321606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100202
Lower baseline amyloid beta burden is associated with greater percent of amyloid beta positron emission tomography reduction and better clinical outcomes in the aducanumab Phase 3 trials ENGAGE and EMERGE in early Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Aducanumab is a human immunoglobulin G1 anti-amyloid beta antibody for early-stage Alzheimer's disease. After the discontinuation of the aducanumab clinical program and market withdrawal, the Phase 3 data were further assessed to characterize the relationship between baseline amyloid beta load, degree of amyloid beta removal, and subsequent clinical outcomes to provide context for future research.
Objectives: This analysis leveraged modelling techniques to impute missing amyloid beta positron emission tomography values and better understand the relationship between baseline amyloid beta positron emission tomography status, amyloid beta positron emission tomography reduction, and clinical outcomes in the aducanumab Phase 3 ENGAGE and EMERGE (NCT02477800/NCT02484547) studies.
Design: Exploratory data analysis.
Setting: A previously developed model which characterized the relationship between aducanumab exposure and amyloid beta positron emission tomography standard uptake value ratio was updated to impute centiloid values for participants not enrolled in the amyloid beta positron emission tomography substudy. Additional clinically-relevant variables were also summarized.
Participants: 1876 participants with baseline amyloid beta positron emission tomography and clinical endpoints in a pooled ENGAGE/EMERGE dataset at week 78.
Intervention: Aducanumab MEASUREMENTS: Amyloid burden measured by centiloids and clinical endpoints.
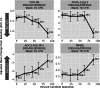
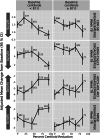
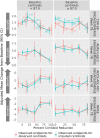
Results: In older participants whose baseline amyloid beta burden is lower than the average trial population, exposure to aducanumab provides greater clinical benefit across cognitive and functional endpoints.
Conclusions: The relationship between baseline amyloid beta load and treatment benefit in a large population after exposure to an amyloid beta-directed antibody provides insight into which subpopulations are likely to benefit from this class of treatment.
Keywords: Amyloid beta centiloids; Clinical outcomes; Exposure-response; Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics; Treatment related amyloid clearance.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Jackson Burton reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Holly M. Brothers reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. R. Matthew Hutchison reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Jennifer Murphy reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Tao Sun reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Gersham Dent reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Gioacchino Curiale reports a relationship with Biogen Inc that includes: employment and equity or stocks. Ken Kowalski reports a relationship with Kowalski PMetrics Consulting that includes: employment. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

