Efficacy of JAK1/2 inhibition in murine myeloproliferative neoplasms is not mediated by targeting oncogenic signaling
- PMID: 40413183
- PMCID: PMC12103521
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-60019-6
Efficacy of JAK1/2 inhibition in murine myeloproliferative neoplasms is not mediated by targeting oncogenic signaling
Abstract
Ruxolitinib is a potent JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, approved for the treatment of primary myelofibrosis (PMF) patients based on the concept of inhibition of oncogenic signaling. However, the effect of ruxolitinib on JAK2-V617F allelic burden is modest, suggesting that inhibition of JAK2-V617F signaling-driven clone expansion is not the main mechanism of action. We evaluate whether ruxolitinib mainly blocks the proliferation of the malignant clone or exerts its effects also by targeting non-malignant cells. Therefore, we develop two JAK2-V617F-driven myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) mouse models harboring ruxolitinib resistance mutations. Mice carrying ruxolitinib-resistant JAK2-V617F-driven MPN respond to ruxolitinib treatment similar to mice with ruxolitinib-sensitive JAK2-V617F MPN with respect to reduction of spleen size, leukocyte count and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the serum. Ruxolitinib reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines in both stromal cells and non-malignant hematopoietic cells. Using a rigorous ruxolitinib resistance mutation approach, we can prove that ruxolitinib acts independent of oncogenic JAK2-V617F signaling and reduces the main features of MPN disease such as spleen size and leukocyte counts. Our findings characterize the mechanism of action for ruxolitinib in MPN.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
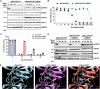
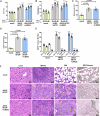
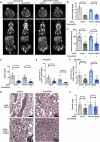
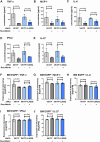
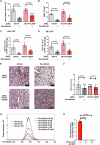
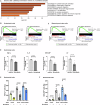
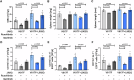
References
-
- Parganas, E. et al. Jak2 is essential for signaling through a variety of cytokine receptors. Cell93, 385–395 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Neubauer, H. et al. Jak2 deficiency defines an essential developmental checkpoint in definitive hematopoiesis. Cell93, 397–409 (1998). - PubMed
-
- James, C. et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature434, 1144–1148 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Baxter, E. J. et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet365, 1054–1061 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SFB-1479, Project ID: 441891347/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- 3554/1-3/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SFB-1479, Project ID: 441891347/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
- SFB-1479, Project ID: 441891347/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (German Research Foundation)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

