Effectiveness of Tildrakizumab 200 mg in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Multicenter Real-World Study Analyzing Patient Outcomes by Weight, PASI, BMI, and Previous Therapies
- PMID: 40413278
- PMCID: PMC12126393
- DOI: 10.1007/s13555-025-01442-x
Effectiveness of Tildrakizumab 200 mg in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Multicenter Real-World Study Analyzing Patient Outcomes by Weight, PASI, BMI, and Previous Therapies
Abstract
Introduction: Psoriasis is a chronic immune-mediated disease with significant systemic implications. Tildrakizumab, an IL-23p19 inhibitor, has demonstrated efficacy in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Higher doses may be beneficial for patients with elevated body weight or greater disease burden. This study evaluates the effectiveness of tildrakizumab 200 mg in a real-world setting, analyzing outcomes based on weight, Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI), body mass index (BMI), and prior biologic exposure.
Methods: A multicenter retrospective study was conducted across 10 Italian hospitals. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis treated with tildrakizumab 200 mg for ≥ 36 weeks were included. Patients were stratified by weight (≥ 90 kg vs. < 90 kg), BMI (≥ 30 vs. < 30), PASI (≥ 15 vs. < 15), and biologic history (naïve vs. biologic (bio)-experienced). PASI100 response rates at 36 weeks were assessed. Statistical analyses included Fisher's exact test (p < 0.05 significant).
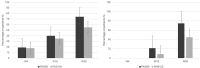
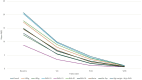
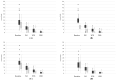
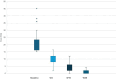
Results: Among 137 patients, PASI100 response rates were 67.1% for patients < 90 kg vs. 49.2% for ≥ 90 kg (p = 0.04), 61.5% for PASI < 15 vs. 50% for PASI ≥ 15 (p = 0.03), and 60.8% for bio-naïve vs. 57.1% for bio-experienced (p = 0.08). BMI ≥ 30 was associated with lower PASI100 (44.2%) compared to BMI < 30 (61.4%) (p = 0.05). Despite subgroup differences, all patients exhibited clinical improvement.
Conclusion: Tildrakizumab 200 mg effectively treated moderate-to-severe psoriasis across diverse patient subgroups. While higher weight and PASI were associated with slightly lower PASI100 rates, significant improvements were observed, supporting its role in difficult-to-treat patients.
Keywords: Biologics; Body mass index; Pasi; Psoriasis; Tildrakizumab; Weight.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Anna Campanati is an Editorial Board member of Dermatology and Therapy. Anna Campanati was not involved in the selection of peer reviewers for the manuscript nor any of the subsequent editorial decisions. Emanuele Trovato has nothing to disclose. Tommaso Bianchelli has nothing to disclose. Giulia Odorici has nothing to disclose. Aldo Cuccia has nothing to disclose. Vito Giuseppe Di Lernia has nothing to disclose. Claudia Lasagni has nothing to disclose. Marco Manfredini has nothing to disclose. Massimiliano Nicolini has nothing to disclose. Giulia Rech has nothing to disclose. Francesca Satolli has nothing to disclose. Alessandra Cartocci has nothing to disclose. Federico Bardazzi has nothing to disclose. Ethical Approval: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964 and subsequent amendments) and it was approved by the local ethics committee (N° 22045).
Figures

References
-
- Armstrong AW, Read C. Pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of psoriasis: a review. JAMA. 2020;323(19):1945–60. 10.1001/jama.2020.4006. - PubMed
-
- Trovato E, Rubegni P, Prignano F. Place in therapy of anti-IL-17 and 23 in psoriasis according to the severity of comorbidities: a focus on cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2022;22(12):1443–8. 10.1080/14712598.2022.2093106. - PubMed
-
- Dragotto M, Capalbo E, Cartocci A, et al. Real-life effectiveness of risankizumab according to body mass index: results of an Italian Multicentre Retrospective Study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. 10.1111/jdv.19117. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

