Unlocking the potential of essential oils in aromatic plants: a guide to recovery, modern innovations, regulation and AI integration
- PMID: 40413718
- PMCID: PMC12104116
- DOI: 10.1007/s00425-025-04724-y
Unlocking the potential of essential oils in aromatic plants: a guide to recovery, modern innovations, regulation and AI integration
Abstract
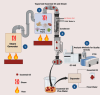
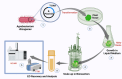
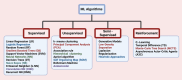
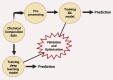
Essential oils recovered from aromatic plants hold tremendous potential across diverse fields, which include therapeutic, industrial, and technological domains. Integrating advanced recovery techniques, regulatory frameworks, and AI-driven innovations can significantly elevate their sustainable production and application. There is a growing need for essential oils (EOs) due to their therapeutic and aromatic benefits, they have been explored across the globe. This comprehensive guide tries to give a glimpse of the skyrocketing potential of EOs by highlighting the advancements in recovery techniques, modern innovations, regulatory frameworks, and its integration with modern technologies like artificial intelligence (AI). The review highlights the importance of quality control in ensuring purity of EOs, discusses various extraction methods, and explores emerging technologies like supercritical fluid extraction and microwave-assisted extraction for successful and quick recovery of EOs with minimal energy requirements. The guide also delves into modern innovations such as encapsulation techniques and nanoemulsion formulations, expanding the scope of essential oils in industries like cosmetics, personal care, and healthcare sector. Addressing the regulatory aspect, the review emphasizes on the standardized quality testing, labeling, and safety considerations necessary for EOs to reach the market. Further, the paper explores the applications of EOs in business innovations such as preservatives to extend shelf life and aromatherapy for pain reduction. Overall, this guide provides valuable insights into the future of EOs, showcasing the possibilities enabled by advancements in techniques, innovations, regulations, and AI integration, benefiting researchers, industry professionals and public.
Keywords: Aromatherapy; Artificial intelligence; Business innovations; Distillation; Essential oils; Machine learning; Tissue culture.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Redefining Mentorship in Medical Education with Artificial Intelligence: A Delphi Study on the Feasibility and Implications.Teach Learn Med. 2025 Jun 18:1-11. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2025.2521001. Online ahead of print. Teach Learn Med. 2025. PMID: 40534163
-
Advancements in AI for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics: A Comprehensive Review.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2952:87-105. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4690-8_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40553329 Review.
-
Striking a Balance: Innovation, Equity, and Consistency in AI Health Technologies.JMIR AI. 2025 Apr 7;4:e57421. doi: 10.2196/57421. JMIR AI. 2025. PMID: 40605778 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap for model-based bioprocess development.Biotechnol Adv. 2024 Jul-Aug;73:108378. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108378. Epub 2024 May 15. Biotechnol Adv. 2024. PMID: 38754797 Review.
-
Current progress in the ginger oleoresin: bioactivities, extraction and encapsulation technologies.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 21:1-20. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2025.2521651. Online ahead of print. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40544325 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activity of Essential Oils from Selected Pinus Species from Bosnia and Herzegovina.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;14(7):677. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14070677. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akbar A, Kuanar A, Patnaik J, Mishra A, Nayak S (2018) Application of artificial neural network modeling for optimization and prediction of essential oil yield in turmeric (Curcuma longa L.). Comput Electron Agric 148:160–178. 10.1016/J.COMPAG.2018.03.002
-
- Aly A, Maraei R, Rezk A, Diab A (2022) Phytochemical constitutes and biological activities of essential oil extracted from irradiated caraway seeds (Carum carvi L.). Int J Radiat Biol 99(2):318–328. 10.1080/09553002.2022.2078004 - PubMed
-
- Al-Zereini WA, Al-Trawneh IN, Al-Qudah MA, Tumallah HM, Abudayeh ZH, Hijazin T (2023) Antibacterial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities of Syzygium aromaticum (L.) Merr. & Perry essential oil with identification of its chemical constituents. Zeitschrift fur Naturforsch Sect C J Biosci 78(3–4):105–112. 10.1515/ZNC-2022-0056/MACHINEREADABLECITATION/RIS - PubMed
-
- An Z, Feng X, Sun M, Wang Y, Wang H, Gong Y (2023) Chamomile essential oil: chemical constituents and antitumor activity in MDA-MB-231 cells through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Chem Biodivers 20(4):e202200523. 10.1002/CBDV.202200523 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

