GP73-dependent regulation of exosome biogenesis promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis
- PMID: 40414849
- PMCID: PMC12105170
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-025-02350-6
GP73-dependent regulation of exosome biogenesis promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis
Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) liver metastasis is the main cause of cancer-related mortality. How liver influences intercellular communication to support CRC liver metastasis remains unknown. Herein, we link GP73, whose chronic upregulation in hepatocytes triggers non-obese metabolic-dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in mice, with exosome biogenesis and CRC liver metastasis. Mice with high liver GP73 expression exhibited increased CRC liver metastasis in an exosome-dependent manner. GP73 modulated the cholesterol contents in endosomal compartments to promote exosome production. Quantitative proteomics revealed GP73 reshaped hepatocyte exosomal proteome and produced NAV2-rich exosomes. Clinically, serum GP73 levels positively correlated with exosomal NAV2 levels in CRC patients with liver metastasis. Knockdown of liver NAV2 suppressed enhanced CRC liver metastasis in GP73-induced non-obese mice, and GP73 blockade mitigated the increased CRC liver metastasis in obese mice fed by high-fat diet or high-fructose diet. Our findings suggest GP73 blockade as a potential therapeutic strategy for mitigating CRC liver metastasis.
GP73 closely correlated with exosome biogenesis and CRC liver metastasis, and GP73 blockade may merit exploration as a potential therapeutic strategy for mitigating CRC liver metastasis.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Exosome; Golgi protein 73; Metastasis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The use of patient samples in this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangxi Medical University Cancer Hospital (LW2023060). All animal experiments were conducted at the AMMS Animal Center (Beijing, China) and were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC-DWZX-2023-022). Consent for publication: All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Notes: No author disclosures were reported. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
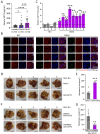

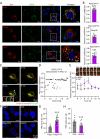





References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32100558/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82360537/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32070755/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81773205/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- GKE-ZZ202004/Key Laboratory of High-Incidence-Tumor Prevention and Treatment, Ministry of Education, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

