A four gene risk score model for prognosis and immune microenvironment insights in small cell lung cancer based on CAF functional-related genes
- PMID: 40415048
- PMCID: PMC12104126
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-025-02781-z
A four gene risk score model for prognosis and immune microenvironment insights in small cell lung cancer based on CAF functional-related genes
Abstract
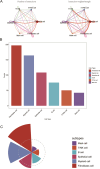
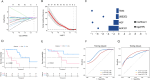
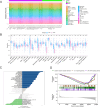
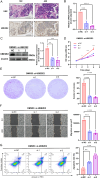
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is still one of the most formidable challenges in oncology. In this study, we introduce an innovative risk scoring model rooted in cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF)-related functional genes, designed to predict patient prognosis and illuminate the microenvironment of SCLC. Through Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, our model could effectively classify patients into high- and low-risk groups, with distinct survival outcomes and remarkable predictive accuracy, which has been evidenced by the AUC values. The low-risk patients showed a more active immune environment, characterized by more infiltration of dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and higher expression of immune co-stimulation molecules. On the contrary, high-risk patients displayed an enrichment of DNA repair and glycolysis pathways associated with tumor aggressiveness and treatment resistance. These results suggest that the risk model offers a nuanced view of response to immunotherapy that may guide the identification of patients who may benefit from immunotherapy. Moreover, we also verified the function of the key gene UBE2E2 by SCLC cell line experiments. Silencing UBE2E2 results in decreased cell proliferation and migration as well as increased apoptosis, which enhances its important role in SCLC biology. In summary, our study highlights the prognostic potential of the CAF-related functional gene risk model and its implications for predicting immune microenvironment status and guiding SCLC treatment strategies.
Keywords: Cancer-associated fibroblast; Predictive model; Small cell lung cancer; Tumor immune microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Zhejiang Cancer Hospital (Approval No. IRB-2024-301) and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was waived by the ethics committee due to the retrospective nature of the study and the use of anonymized archival specimens. Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
