Illuminating extracellular nanovesicles through the spectroscopic lens: a mini review of cutting-edge insights and emerging applications
- PMID: 40416313
- PMCID: PMC12098046
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1592391
Illuminating extracellular nanovesicles through the spectroscopic lens: a mini review of cutting-edge insights and emerging applications
Abstract
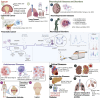
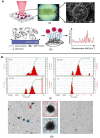
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are cell-derived particles that facilitate intercellular communication by carrying bioactive molecules like proteins and RNA, impacting both health and disease. Herein, the EVs' significance in physiological and pathological processes is reviewed, emphasising their potential as biomarkers for diseases including for instance, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and cardiovascular conditions. The principles and applications of Raman spectroscopy (RS) - a powerful tool offering detailed molecular insights into EVs, are further examined. The non-destructive nature of this spectroscopic technique renders it invaluable for studying the molecular composition, purity and concentration of EVs. When EVs are isolated from accessible biofluids such as blood, urine or saliva, the overall process remains minimally invasive, enhancing its clinical applicability. The review highlights Raman spectroscopy's role in identifying disease-related EVs, distinguishing subpopulations and enhancing our understanding of EVs in disease mechanisms and therapeutic applications.
Keywords: Raman imaging; Raman spectroscopy; SERS (surface enhanced Raman scattering); disease diagnostics; extracellular vesicles.
Copyright © 2025 Bhowmik, Patel and Goldberg Oppenheimer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Banwell C. N. (1972). Fundamentals of molecular spectroscopy.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

