Hand functional capacity in women with systemic sclerosis using the Glittre-ADL-Shelf test: Relationship with demographics, body composition, hand function, physical function, digital dexterity, muscle strength and lung function
- PMID: 40416411
- PMCID: PMC12102079
- DOI: 10.1177/23971983251341515
Hand functional capacity in women with systemic sclerosis using the Glittre-ADL-Shelf test: Relationship with demographics, body composition, hand function, physical function, digital dexterity, muscle strength and lung function
Abstract
Objective: Hand functionality in systemic sclerosis is assessed using patient-reported measures. However, the Glittre-ADL test (TGlittre) provides an objective assessment of functional capacity using activities of daily living, including the hand shelf task. The aim of this study was to assess hand functional capacity in women with systemic sclerosis using the TGlittre-Shelf and to correlate it with demographics, body composition, hand function, physical function, digital dexterity, muscle strength, and lung function.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional study in which 41 women with systemic sclerosis and 41 healthy controls underwent the TGlittre-S. They also underwent the following assessments: Cochin Hand Functional Scale, modified Rodnan skin score, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index, 9-hole peg test, handgrip strength, and pulmonary function tests.
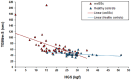
Results: The mean age was 51.9 ± 13.7 and 45.9 ± 9.3 years in women with systemic sclerosis and healthy controls, respectively (p = 0.09). Body mass index was 24.4 ± 4.9 and 29.4 ± 5.3 kg/m2 in women with systemic sclerosis and healthy controls, respectively (p < 0.0001). TGlittre-S time was higher in women with systemic sclerosis than in healthy controls [60 (55-74) vs 44 (41-49) sec, p < 0.0001]. In addition, 9-hole peg test was higher in women with systemic sclerosis than in healthy controls [24 (22-26) vs 20 (18-22) sec, p < 0.0001]. Similarly, Cochin Hand Functional Scale was higher in women with systemic sclerosis than in healthy controls [6 (0.5-25) vs 0 (0-0) points, p < 0.0001]. In women with systemic sclerosis, TGlittre-S time was significantly correlated with the following variables: handgrip strength (rs = -0.511, p = 0.0006), Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (rs = 0.510, p = 0.0006), 9-hole peg test (rs = 0.398, p = 0.009), and Cochin Hand Functional Scale (rs = 0.351, p = 0.024).
Conclusion: In women with systemic sclerosis, there is a deterioration in impaired hand functional capacity as measured by TGlittre-S. In these patients, the longer the TGlittre-S time, the worse the handgrip strength, digital dexterity, and physical function. As TGlittre-S is easy to perform and does not require much space, its incorporation into clinical practice is promising and may be considered as an outcome measure for future studies in systemic sclerosis.
Keywords: Systemic sclerosis; exercise; functional capacity; hand; pulmonary function.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional Capacity Incorporating Dynamic Ventilation in Systemic Sclerosis: Agreement Analysis Between Performance on the 6-Minute Walk Test and Glittre-ADL Test.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2025 Mar;38(2):294-303. doi: 10.1177/10538127241298551. Epub 2025 Jan 9. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 39973265
-
Evaluating the contribution of the Glittre-ADL test in adults with cystic fibrosis.Physiother Res Int. 2024 Apr;29(2):e2087. doi: 10.1002/pri.2087. Physiother Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38551092
-
Home-based rehabilitation improves functional capacity and quality of life in women with systemic sclerosis: A preliminary study.J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023;36(2):455-463. doi: 10.3233/BMR-220077. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 36155500
-
Long-term assessment of functional capacity, muscle function, lung function, and quality of life in survivors of ventilator-associated pneumonia.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 9;10(1):e23431. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23431. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38169824 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Glittre-ADL test in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: Pre- and postoperative analysis after home-based rehabilitation: A preliminary study.Heliyon. 2024 Nov 22;10(23):e40646. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e40646. eCollection 2024 Dec 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39654716 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effects of a 12-week physiotherapist-supervised home-based rehabilitation program on the functional exercise capacity in people with systemic sclerosis.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2025 Jul 28:23971983251360912. doi: 10.1177/23971983251360912. Online ahead of print. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2025. PMID: 40746332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mouthon L. [Hand involvement in systemic sclerosis]. Presse Med 2013; 42(12): 1616–1626. - PubMed
-
- Fourmond S, Parreau S, Dumonteil S, et al.. The functional disabilities of the dominant and opposite hands in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2024; 42(8): 1665–1668. - PubMed
-
- Moinzadeh P, Bonella F, Oberste M, et al.. Impact of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease with and without pulmonary hypertension on survival: a large cohort study of the german network for systemic sclerosis. Chest 2024; 165(1): 132–145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
