Hydrogen sulfide protects against cisplatin-induced experimental nephrotoxicity in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40416612
- PMCID: PMC12103845
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19481
Hydrogen sulfide protects against cisplatin-induced experimental nephrotoxicity in animal models: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury (cis-AKI) is not rare in oncological patients clinically, but there are limited prevention and treatment methods available. The efficacy of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in mitigating cis-AKI has been studied and determined in animal models.
Methods: According to the pre-registered program (PROSPERO: CRD 42023463779), we searched PubMed/Medline, Embase, and Web of Science databases using the keywords: hydrogen sulfide, cisplatin, acute kidney injury, and alternatives. A total of 13 articles met the inclusion criteria were included. Standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were calculated and aggregated using random effects meta-analysis.
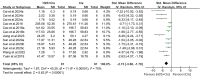
Results: The results showed that H2S treatment significantly improved renal function (serum creatinine SMD = -2.96, 95% CI [-3.72 to -2.19], p < 0.00001; blood urea nitrogen SMD = -2.73, 95% CI [-3.68 to -1.78], p < 0.00001), decreased oxidative stress (superoxide dismutase SMD = 2.90, 95% CI [1.36-4.43], p = 0.0002) and inflammation levels (interleukin-1β SMD = -4.41, 95% CI [-5.84 to -2.97], p < 0.00001). However, there was a high degree of heterogeneity between studies (I2 > 70%). Further subgroup analysis did not show a clear source of the heterogeneity, but various H2S donors exhibited positive renal protection in those studies.
Conclusions: H2S could be a new approach for treating cis-AKI, while the differential efficacies among natural and slow-release H2S donors remain to be compared and evaluated further. This meta-analysis may shed light on establishing preclinical and clinical investigation guidelines for treating human cis-AKI with H2S donors.
Keywords: Cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury; Experimental nephrotoxicity; Hydrogen sulfide; Vivo studies.
© 2025 Han et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Psychological and/or educational interventions for the prevention of depression in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Dec 07;(12):CD003380. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003380.pub3. PMID: 14974014 Updated.
-
Aromatherapy for treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 10;3(3):CD007598. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007598.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29523018 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7(7):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub4. PMID: 28752910 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Abdel-Daim MM, Abdel-Rahman HG, Dessouki AA, El-Far AH, Khodeer DM, Bin-Jumah M, Alhader MS, Alkahtani S, Aleya L. Impact of garlic (Allium sativum) oil on cisplatin-induced hepatorenal biochemical and histopathological alterations in rats. Science of the Total Environment. 2020;710(4):136338. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136338. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Daim MM, Abushouk AI, Donia T, Alarifi S, Alkahtani S, Aleya L, Bungau SG. The nephroprotective effects of allicin and ascorbic acid against cisplatin-induced toxicity in rats. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2019;26(13):13502–13509. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04780-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmad FU, Sattar MA, Rathore HA, Abdullah MH, Tan S, Abdullah NA, Johns EJ. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) reduces blood pressure and prevents the progression of diabetic nephropathy in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Renal Failure. 2012;34(2):203–210. doi: 10.3109/0886022x.2011.643365. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

