Prognostic significance of C-reactive protein (CRP) and albumin-based biomarker in patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy
- PMID: 40416620
- PMCID: PMC12103165
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.19319
Prognostic significance of C-reactive protein (CRP) and albumin-based biomarker in patients with breast cancer receiving chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer patients with similar clinicopathologic characteristics may experience varied outcomes. This urges an increased effort to investigate other prognostic factors. C-reactive protein (CRP)-to-albumin ratio (CAR) is an inflammatory and nutritional biomarker that has been well studied and reported to have an impact on the survival of patients with diverse types of cancer, but limitedly in breast cancer. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the prognostic significance of CAR in local patients with breast cancer.
Methods: This study included 202 stage I-IV breast cancer patients receiving first-line chemotherapy. We calculated inflammatory and nutritional biomarkers including CAR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), systemic inflammation response index (SIRI), pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV), and prognostic nutrition index (PNI) before treatment. The Kaplan-Meier with log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard regression were used to analyze the prognostic role of clinicopathologic factors and biomarkers on disease-free survival (DFS), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS).
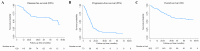
Results: The median follow-up period was 46 months (1-77 months). The 3-year DFS and 3-year OS in patients with high CAR (CAR > 1.5) were significantly lower than those with low CAR (CAR ≤ 1.5) (47.0% vs 68.9%, P = 0.022 and 59.5% vs 78.6%, P = 0.009, respectively). Multivariate analysis showed high CAR as prognostic factors for poor DFS (HR 2.10, 95% confidence interval/CI [1.10-3.99], P = 0.023) and OS (HR 2.16, 95% CI [1.27-3.68], P = 0.005), but not for PFS (HR 1.43, 95% CI [0.73-2.80], P = 0.293). In addition, more advanced stage and HER2 positive were correlated with unfavorable DFS and OS, older age predicted poor DFS, and stage was the only prognostic factor of PFS (all P values < 0.05).
Conclusion: Besides age, stage, and molecular subtypes that have been widely observed to have impact on the survival of breast cancer patients, CAR was demonstrated as a promising prognostic marker in our local patients. A high CAR at diagnosis was associated with unfavorable DFS and OS, which can aid in identifying patients at risk and guide personalized treatment planning.
Keywords: Albumin; Breast neoplasms; C-reactive protein; Mortality; Survival.
©2025 Hutajulu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, Harewood R, Matz M, Nikšić M, Bonaventure A, Valkov M, Johnson CJ, Estève J, Ogunbiyi OJ, Azevedo E Silva G, Chen WQ, Eser S, Engholm G, Stiller CA, Monnereau A, Woods RR, Visser O, Lim GH, Aitken J, Weir HK, Coleman MP, CONCORD Working Group Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391:1023–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

