Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value as a Prognostic Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Hepatectomy
- PMID: 40416712
- PMCID: PMC12103170
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S521603
Pan-Immune-Inflammation Value as a Prognostic Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Hepatectomy
Abstract
Purpose: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) poses a substantial threat to global health, characterized by its high incidence and mortality rates. This research aims to assess the prognostic value of a systematic serum inflammation index, the pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV), in patients with HCC who have undergone hepatectomy.
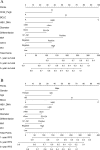
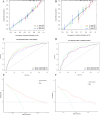
Patients and methods: A total of 1764 HCC patients who underwent surgery were included in the study. These patients were divided into two groups based on the median PIV value. The Cox regression model was utilized to ascertain the independent risk factors that influence the prognosis of patients. A PIV-based nomogram was constructed and its performance was evaluated by the C-index, calibration curve, ROC curve, and DCA curve. Finally, a comparison was made between the nomogram and existing staging models.
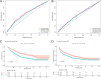
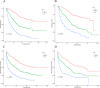
Results: Patients with elevated PIV exhibited diminished OS and RFS compared to those with lower PIV. Univariate and multivariate Cox analyses revealed that PIV is an independent predictor of prognosis. The PIV-based nomogram demonstrated excellent discrimination, calibration, and clinical net benefit. The proposed nomogram outperformed the other existing staging systems, as evidenced by a higher AUC value.
Conclusion: PIV exhibits potential as a prognostic factor for both OS and RFS in patients with HCC who have undergone hepatectomy. The PIV-based nomogram can serve as an additional tool in conjunction with the existing liver cancer staging system, thereby facilitating more personalized treatment decisions for clinicians.
Keywords: hepatectomy; hepatocellular carcinoma; pan-immune- inflammation value; prognosis.
© 2025 Fu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose in connection with this research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prognostic significance of pan-immune-inflammation value in hepatocellular carcinoma treated by curative radiofrequency ablation: potential role for individualized adjuvant systemic treatment.Int J Hyperthermia. 2024;41(1):2355279. doi: 10.1080/02656736.2024.2355279. Epub 2024 May 20. Int J Hyperthermia. 2024. PMID: 38767372
-
Prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index/albumin for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma undergoing curative resection.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Dec 28;30(48):5130-5151. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i48.5130. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39735268 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of inflammation and nutritional index in immunotherapy for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer and model construction.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 30;14(1):17511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66813-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080372 Free PMC article.
-
Development of nomogram models of inflammatory markers based on clinical database to predict prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection.BMC Cancer. 2022 Mar 7;22(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09345-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35255845 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of pan-immune-inflammation value (PIV) in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 19;10(2):e24804. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24804. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang L, Li C, Wang MD, et al. Development and validation of a novel online calculator for estimating survival benefit of adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients undergoing surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma. J hematol oncol. 2021;14(1):165. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01180-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

