Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) treatment on age-related cognitive decline in C57 mice
- PMID: 40416734
- PMCID: PMC12098523
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1567650
Effects of cannabidiol (CBD) treatment on age-related cognitive decline in C57 mice
Abstract
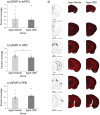
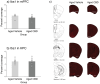
Aging is associated with cognitive decline, and currently, there are no approved medications that can prevent these impairments. Recently, cannabinoids derived from Cannabis sativa have emerged as promising therapeutic compounds with neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and cognitive-enhancing properties. Despite their benefits, further research is needed to fully understand their efficacy across various conditions. This study investigates the effects of cannabidiol (CBD) on memory impairment and brain inflammation in aging mice. Fourteen-month-old C57 mice were administered CBD orally for 7 months and subsequently evaluated between 19 and 21 months of age using behavioral tasks that are sensitive to dysfunction of the perirhinal cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, and various brain regions that are crucial for motor control and coordination. The findings of this study indicate that CBD reduces inflammatory response in the brain and improves cognitive decline associated with aging.
Keywords: acetylcholine; age-related cognitive decline; aging; cannabidiol (CBD); hippocampus; inflammation; learning and memory; prefrontal cortex.
Copyright © 2025 Mirza Agha, Monteith, Earl, Ganske, Kaloa, McDonald, Nixon, Panjwani, Robinson, Rusnak, Mohajerani, Kovalchuk, Sutherland, Hong and McDonald.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures




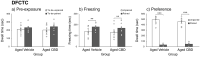


References
-
- Abame M. A., He Y., Wu S., Xie Z., Zhang J., Gong X., et al. . (2021). Chronic administration of synthetic cannabidiol induces antidepressant effects involving modulation of serotonin and noradrenaline levels in the hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 744:135594. 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135594 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

