Connection and happiness: an interactive study of social media, social capital, and the subjective well-being of international students
- PMID: 40417013
- PMCID: PMC12098500
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1548663
Connection and happiness: an interactive study of social media, social capital, and the subjective well-being of international students
Abstract
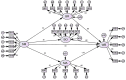
The subjective well-being of international students is crucial for their adaptation and academic success in a foreign country. Based on online social capital theory, this study examines how social media use affects the subjective well-being of international students and explores the underlying mechanisms and the moderating role of college attachment. A questionnaire survey was conducted among 21 universities in China, yielding 474 valid responses, which were analyzed using structural equation modeling. The findings indicate that social media use significantly and positively predicts the subjective well-being of international students, as well as bridging, bonding, and maintaining social capital. Notably, only bonding social capital partially mediates the relationship between social media use and subjective well-being. Additionally, college attachment positively moderates the indirect effect of bridging social capital only, but it did not significantly moderate the relationship between social media use and subjective well-being. These results highlight that social media use can enhance the subjective well-being of international students through social capital. This effect is moderated by college attachment, providing valuable insights for relevant stakeholders.
Keywords: college attachment; international student; social capital; social media; subjective well-being.
Copyright © 2025 Duan, Lu and Lyu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- An R., Chen W. (2017). Research on social support of mobile social media to international students. J. Xinjiang Normal Univ. (Philos. Soc. Sci. Ed.) 38, 131–137. doi: 10.14100/j.cnki.65-1039/g4.2017.01.013 - DOI
-
- Billedo C. J., Kerkhof P., Finkenauer C., Ganzeboom H. (2019). Facebook and face-to-face: examining the short- and long-term reciprocal effects of interactions, perceived social support, and depression among international students. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 24, 73–89. doi: 10.1093/jcmc/zmy025 - DOI
-
- Boyd D. M., Ellison N. B. (2007). Social network sites: definition, history, and scholarship. J. Comput.-Mediat. Commun. 13, 210–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1083-6101.2007.00393.x - DOI
-
- Bukhari S., Hamid S., Ravana S. D., Kurnia S., Chang S., Norman A. A., et al. (2020). The use of Facebook by international students for information-seeking in Malaysia: a social network analysis. Libri Int. J. Libr. Inf. Stud. 70, 251–268. doi: 10.1515/libri-2019-0033, PMID: - DOI
-
- Chen H. T., Li X. (2017). The contribution of mobile social media to social capital and psychological well-being: examining the role of communicative use, friending and self-disclosure. Comput. Hum. Behav. 75, 958–965. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.011 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources