Engineered exosomes: a promising drug delivery platform with therapeutic potential
- PMID: 40417062
- PMCID: PMC12098103
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1583992
Engineered exosomes: a promising drug delivery platform with therapeutic potential
Abstract
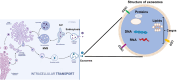
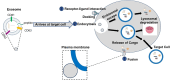
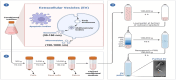
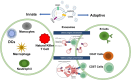
Exosomes, small membranous vesicles naturally secreted by living cells, have garnered attention for their role in intercellular communication and therapeutic potential. Their low immunogenicity, high biocompatibility, and efficient biological barrier penetration make them promising drug delivery vehicles. This review spans research developments from 2010 to 2025, covering the engineering of exosomes to optimize cargo loading and targeting specificity. We discuss their applications in treating cardiovascular diseases, liver fibrosis, immune diseases, and neurological diseases, alongside ongoing clinical trials and industry progress. Future challenges include scalability, standardization, and minimizing off-target effects. We propose strategies to address these hurdles, such as bioengineering techniques and improved isolation methods. By synthesizing current knowledge and outlining future directions, this review aims to guide researchers toward harnessing exosomes for disease treatment.
Keywords: Exosomes; and nervous disorders; cardiovascular diseases; immune diseases; liver fibrosis.
Copyright © 2025 Schwarz, Ren, Xie, Guo, Jiang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures


References
-
- Alshanwani A. R., Hagar H., Shaheen S., Alhusaini A. M., Arafah M. M., Faddah L. M., et al. (2022). A promising antifibrotic drug, pyridoxamine attenuates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis by combating oxidative stress, advanced glycation end products, and balancing matrix metalloproteinases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 923, 174910. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174910 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

