Global Burden of Kidney Cancer Attributable to High Body Mass Index in Adults Aged 60 and Older from 1990 to 2021 and Projections to 2040: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study
- PMID: 40417134
- PMCID: PMC12103881
- DOI: 10.2147/CLEP.S521272
Global Burden of Kidney Cancer Attributable to High Body Mass Index in Adults Aged 60 and Older from 1990 to 2021 and Projections to 2040: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study
Abstract
Background: With global aging, cancer burden rises. Kidney cancer is significantly influenced by high body mass index (BMI), especially in the elderly. This study analyzes the burden of kidney cancer attributable to high BMI in those aged ≥60, clarifying causes and future trends.
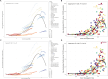
Methods: Using Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 study, we assessed kidney cancer burden due to high BMI in population aged ≥60 from 1990 to 2021, comparing deaths, disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), age-standardized rate (ASR) of DALYs (ASDR), and mortality (ASMR). Stratified by Socio-Demographic Index (SDI), region, sex, and age, we evaluated spatiotemporal trends and inequalities. Finally, the Bayesian Age-Period-Cohort (BAPC) model predicted burden changes through 2040.
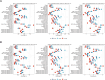
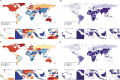
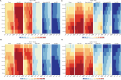
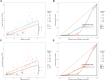
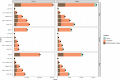
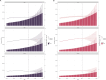
Results: From 1990 to 2021, DALYs and deaths from high BMI-induced kidney cancer in those aged ≥60 increased by 165.82% and 186.39%, driven by population growth. In 2021, ASDR was 45.55/100,000 and ASMR 2.39/100,000. Regional differences were significant. DALYs and deaths expanded, especially in those aged ≥95. Males had higher burden than females. SDI correlated positively with ASDR and ASMR (r>0, P<0.05). Health inequalities continue to rise. By 2040, burden is projected to rise, especially in low-middle and low SDI regions, more in males.
Conclusion: This study shows a significant increase in kidney cancer burden due to high BMI in those aged ≥60 over 32 years, driven by population growth. Disparities across regions, genders, and age groups highlight the need for targeted prevention and early intervention, especially for high-risk groups (males, elderly, low-middle SDI regions), to reduce burden and optimize healthcare resource allocation.
Keywords: SDI; elderly; gender differences; high BMI; kidney cancer; trend projection.
© 2025 Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease attributable to high sodium intake from 1990 to 2019.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 2;10:1078371. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1078371. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 36937353 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and predictions of the global burden of ischemic heart disease in women of childbearing age attribute to high body mass index and hypertension,1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025 May 9;25(1):360. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04741-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2025. PMID: 40346517 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of colorectal cancer attributable to diet low in whole grains from 1990 to 2021: a global, regional and national analysis.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 9;12:1527522. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1527522. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40271437 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden, risk factors, and projections of early-onset dementia: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Ageing Res Rev. 2025 Feb;104:102644. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102644. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Ageing Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39701185 Review.
-
Global, regional, and national burdens of pancreatic cancer attributable to smoking from 1990 to 2021 and the projections to 2035:a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021.Front Oncol. 2025 May 30;15:1547029. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1547029. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40519307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vasudev NS, Wilson M, Stewart GD, et al. Challenges of early renal cancer detection: symptom patterns and incidental diagnosis rate in a multicentre prospective UK cohort of patients presenting with suspected renal cancer. BMJ Open. 2020;10(5):e35938. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2019-035938 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

