Establishing cell polarity in plants: the role of cytoskeletal structures and regulatory pathways
- PMID: 40417180
- PMCID: PMC12098400
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1602463
Establishing cell polarity in plants: the role of cytoskeletal structures and regulatory pathways
Abstract
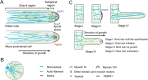
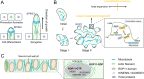
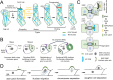
Cell polarity is a fundamental mechanism of plant cells that drives cellular specialization and the formation of diverse cell types. It regulates critical developmental events, including polarized tip growth (such as pollen tubes and root hairs), epidermal patterning (such as trichome branching and asymmetric cell division in stomata). The establishment and maintenance of cell polarity rely on the cytoskeleton-mediated polarized distribution of specific proteins and organelles. In particular, cell-type-specific actin and microtubule dynamic structures are pivotal for maintaining polarity. For example, actin cables and short actin fragments are critical for pollen tube growth, while actin clusters and microtubule rings are involved in trichome branching, and actin patches contribute to stomatal mother cell polarization. Beyond directing the polarization of organelles and proteins, the cytoskeleton itself serves as an intrinsic cue for polarity. For instance, actin patches in stomatal precursor cells act as self-organizing polarity landmarks. Despite the diversity of cytoskeletal structures and their functions, common regulators, such as Rop GTPase signaling pathways, WAVE/SCAR complexes, and motor proteins regulate the assembly and function of these structures. Recent advances have revealed new regulatory mechanisms, such as microtubule exclusion zones guiding asymmetric divisions during Arabidopsis stomatal development, and the role of actin rings in regulating xylem pit formation. These discoveries contribute to a deeper understanding of the cytoskeleton's crucial role in polarity regulation. In this review, we highlight the key cytoskeletal structures involved in the establishment of cell polarity in plants and discuss the molecular mechanisms underlying their spatiotemporal assembly. We also address emerging questions regarding the cytoskeleton's role in cell polarity and development.
Keywords: actin; cell polarity; microtubule; polarity proteins; polarity regulation.
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Chang, Hazelwood, Arif Ashraf and Nan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Focusing on the focus: what else beyond the master switches for polar cell growth?Mol Plant. 2015 Apr;8(4):582-94. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2014.12.023. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Mol Plant. 2015. PMID: 25744359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction Between Actin and Microtubules During Plant Development.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2025 Apr 16. doi: 10.1002/cm.22029. Online ahead of print. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40237573 Review.
-
Investigation of ROP GTPase Activity and Cytoskeleton Dynamics During Tip Growth in Root Hairs and Pollen Tubes.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2604:227-235. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2867-6_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36773237
-
ROP GTPase-dependent polarity establishment during tip growth in plants.New Phytol. 2022 Oct;236(1):49-57. doi: 10.1111/nph.18373. Epub 2022 Jul 27. New Phytol. 2022. PMID: 35832004 Review.
-
Arabidopsis formin3 directs the formation of actin cables and polarized growth in pollen tubes.Plant Cell. 2009 Dec;21(12):3868-84. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.068700. Epub 2009 Dec 18. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 20023198 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

