Delineating Neuroanatomical Structures for the Measurement of Temporal Horn Dilatation
- PMID: 40417207
- PMCID: PMC12097160
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms-01-2025-077
Delineating Neuroanatomical Structures for the Measurement of Temporal Horn Dilatation
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures

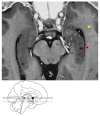

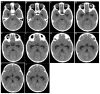
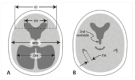

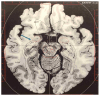
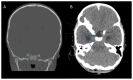
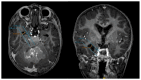
Comment on
-
The Key Aspects of Neonatal and Infant Neurological Examination: The Ballard Score, the Infant's Head with Hydrocephalus and Assessment in a Clinical Setting.Malays J Med Sci. 2023 Aug;30(4):193-206. doi: 10.21315/mjms2023.30.4.16. Epub 2023 Aug 24. Malays J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37655147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zakaria Z, Van Rostenberghe H, Ramli N, Suhaimi MS, Hazlan SNH, Abdullah JM. The key aspects of neonatal and infant neurological examination: the Ballard score, the infant’s head with hydrocephalus and assessment in a clinical setting. Malays J Med Sci. 2023;30(4):193–206. doi: 10.21315/mjms2023.30.4.16. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duvernoy H, Cattin F, Risold P. The human hippocampus: functional anatomy, vascularization and serial sections with MRI. 4th ed. Heidelberg: Springer; 2013. - DOI
-
- Greenberg MS. Greenberg’s handbook of neurosurgery. 10th ed. New York: Thieme; 2023.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
