Suppressing chondrocyte cuproptosis by syringaresinol-4- O- β-d-glucoside alleviates gouty arthritis
- PMID: 40417211
- PMCID: PMC12099060
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565422
Suppressing chondrocyte cuproptosis by syringaresinol-4- O- β-d-glucoside alleviates gouty arthritis
Abstract
Background: Gouty arthritis is a rheumatic disease characterized by synovial inflammation and cartilage damage. Current therapeutic options for gouty arthritis, such as colchicine, primarily relieve the symptoms, which makes treatment challenging.
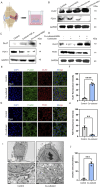
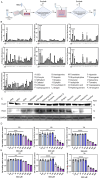
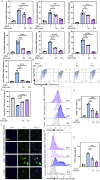
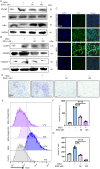
Methods: We employed an in vitro co-culture system of chondrocytes and macrophages to simulate gouty arthritis and screen compounds that can inhibit monosodium urate (MSU) associated macrophage inflammation and chondrocytes degeneration. We further elucidated the cuproptosis mechanism in chondrocytes by qPCR and Western blotting analyses. Both acute and chronic gouty arthritis mouse models were established to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of candidate drugs against gouty arthritis.
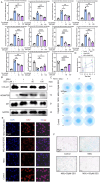
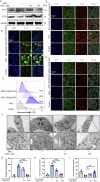
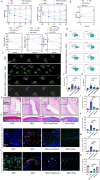
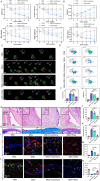
Results: MSU upregulates the expression of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages and simultaneously induces cuproptosis in chondrocytes. By screening 24 compounds, we identified syringaresinol-4-O-β-d-glucoside (SSG), a furanoid lignan, as a potent inhibitor of macrophage-mediated inflammation and chondrocyte cuproptosis. Mechanistically, SSG inhibited MSU-induced activation of the NF-κB and NLRP3 pathways in macrophages. Furthermore, SSG regulated the expression of sulfur-linked mitochondrial enzymes (e.g., DLAT) in the cuproptosis pathway, thereby inhibiting the upstream regulator FDX1 in chondrocytes. SSG not only alleviated inflammatory pain but also protected against cartilage damage and improved motor dysfunction in the mice models of acute and chronic gouty arthritis.
Conclusion: SSG can serve as a promising therapeutic option for gouty arthritis in clinical settings by suppressing inflammation and preserving cartilage integrity.
Keywords: chondrocyte; cuproptosis; gouty arthritis; inflammatory cytokines; monosodium urate crystals; syringaresinol-4-O-β-D-glucoside.
Copyright © 2025 Fu, Du, Ling, Wang, Chen, Zhang, Chen, Liu, Ma, Lin, Ma and Qin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin ameliorates monosodium urate-induced gouty arthritis through Nod-like receptor 3 inflammasome mediation via inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B signaling.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):6718-6728. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27969. Epub 2018 Dec 28. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30592318
-
Anemoside B4 targets NEK7 to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation and alleviate MSU-induced acute gouty arthritis by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Mar;138:156407. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156407. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39939033
-
Total glucosides of paeony protects THP-1 macrophages against monosodium urate-induced inflammation via MALAT1/miR-876-5p/NLRP3 signaling cascade in gouty arthritis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111413. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111413. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33677310
-
Ameliorative Effects of Cardamonin on Monosodium Urate-Induced Gouty Arthritis through Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediation.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Aug 28;57(9):898. doi: 10.3390/medicina57090898. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34577821 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional herbal medicine: Therapeutic potential in acute gouty arthritis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Aug 10;330:118182. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118182. Epub 2024 Apr 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38621464 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

