Construction and validation of a meropenem-induced liver injury risk prediction model: a multicenter case-control study
- PMID: 40417215
- PMCID: PMC12098429
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1542554
Construction and validation of a meropenem-induced liver injury risk prediction model: a multicenter case-control study
Abstract
Objective: To construct and validate a risk prediction model for patients with meropenem-induced liver injury (MiLI).
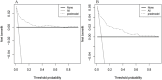
Methods: A retrospective case-control study was conducted to collect data on inpatients treated with meropenem at Shiyan People's Hospital, Hubei, China from January 2018 to December 2022; this study served as the model construction dataset. Univariate analysis and multiple logistic regression analysis were employed to identify the related factors for MiLI, and a nomogram risk prediction model for MiLI was constructed. The recognition ability and prediction accuracy of the model were evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and calibration curves. The clinical efficacy was assessed via the decision curve analysis (DCA). The internal validation was performed using the bootstrap method, and external validation was conducted based on an external dataset from Shiyan Taihe Hospital between October 2021 and December 2023.
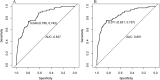
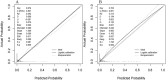
Results: A total of 1,625 individuals were included in the model construction dataset, of which 62 occurred MiLI. The external validation dataset included 1,032 cases, with 74 patients developing liver injury. Six variables were independent factors for MiLI and included in the final prediction model: being male (OR = 2.080, 95% CI: 1.050-4.123, P = 0.036), ICU admission (OR = 8.207, 95% CI: 4.094-16.453, P < 0.001), gallbladder disease (OR = 8.240, 95% CI: 3.605-18.832, P < 0.001), baseline ALP (OR = 1.012, 95% CI: 1.004-1.019, P = 0.004), GGT (OR = 1.010, 95% CI: 1.005-1.015, P < 0.001), and PLT (OR = 0.997, 95% CI: 0.994-0.999, P = 0.020). The c-statistic value for internal validation of the prediction model was 0.821; the sensitivity and specificity were 0.997 and 0.924, respectively. The c-statistic value of the prediction model in the model construction dataset was 0.837 (95% CI, 0.789-0.885), while in the external validation dataset was 0.851 (95% CI, 0.802-0.901). The P-values of the calibration curve in the two datasets were 0.935 and 0.084, respectively.
Conclusion: Being male, ICU admission, gallbladder disease, higher levels of baseline ALP and GGT, and lower levels of baseline PLT were the risk factors for MiLI. The nomogram model built based on these factors demonstrated favorable performance in discrimination, calibration, clinical applicability, and internal-external validation. The nomogram model can assist clinicians in early identification of high-risk patients receiving meropenem, predicting the risk of MiLI, and ensuring safe medication practices.
Keywords: adverse drug reaction; drug safety; drug-induced liver injury; meropenem; prediction model; risk factor.
Copyright © 2025 He, Ke, Zhu, Yuan, Li, Wu, Yang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Establishment and Validation of a Predictive Model for Gallstone Disease in the General Population: A Multicenter Study].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):641-652. doi: 10.12182/20240560501. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948266 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Construction and validation of a predictive model for early occurrence of lower extremity deep venous thrombosis in ICU patients with sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 May;36(5):471-477. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231117-00985. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 38845492 Chinese.
-
Construction and evaluation of a mortality prediction model for patients with acute kidney injury undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy based on machine learning algorithms.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2388709. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2388709. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39155811 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factor analysis and predictive model construction of lean MAFLD: a cross-sectional study of a health check-up population in China.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 25;30(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02373-1. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40001266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic models for newly-diagnosed chronic lymphocytic leukaemia in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 31;7(7):CD012022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012022.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32735048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dai X. Y., Zheng Y. Y., Tang J. N., Wang W., Guo Q. Q., Yin S. S., et al. (2021). Alkaline phosphatase-to-albumin ratio as a novel predictor of long-term adverse outcomes in coronary artery disease patients who underwent PCI. Biosci. Rep. 41 (7), BSR20203904. 10.1042/BSR20203904 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

