The role of ERK1/2 signaling in diabetes: pathogenic and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 40417223
- PMCID: PMC12098375
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1600251
The role of ERK1/2 signaling in diabetes: pathogenic and therapeutic implications
Abstract
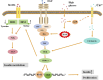
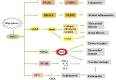
ERK1/2 (extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2) is an important member of the MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) family and is widely involved in many biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and migration. After activation by phosphorylation, ERK1/2 can be transferred into the nucleus and directly or indirectly affect the activity of transcription factors, thereby regulating gene expression. More and more studies have shown that ERK1/2 plays an important role in diabetes and its complications, such as insulin secretion, islet β cell function, diabetic cardiomyopathy, diabetic nephropathy, renal fibrosis, lipogenesis, diabetic vasculopathy, etc. These effects reveal the complexity and diversity of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of diabetes, and its activation and inhibition mechanisms in multiple physiological and pathological processes provide potential targets for diabetes treatment. The purpose of this mini-review is to explore the key role of ERK1/2 in diabetes and the progress of research on targeted inhibitors of ERK1/2, which provides new strategies for the treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: ERK1/2; MAPK; complications; diabetes; inhibitors.
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Liu, Dai, Li and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of ERK1/2 in the Development of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 8;17(12):2001. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122001. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27941647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in myostatin-regulated differentiation repression.Cancer Res. 2006 Feb 1;66(3):1320-6. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3060. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16452185
-
Direct and indirect interactions between calcineurin-NFAT and MEK1-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathways regulate cardiac gene expression and cellular growth.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Feb;25(3):865-78. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.3.865-878.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15657416 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular superoxide dismutase ameliorates streptozotocin-induced rat diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting the ROS/ERK1/2 signaling.Life Sci. 2015 Aug 15;135:77-86. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.04.018. Epub 2015 May 23. Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26006040
-
Control of MAP kinase signaling to the nucleus.Chromosoma. 2005 Jul;114(2):86-91. doi: 10.1007/s00412-005-0341-9. Epub 2005 May 18. Chromosoma. 2005. PMID: 15902482 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

