Efficacy of electroacupuncture treatment for generalized anxiety disorder related insomnia: a study protocol for randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40417269
- PMCID: PMC12098578
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1532001
Efficacy of electroacupuncture treatment for generalized anxiety disorder related insomnia: a study protocol for randomized controlled trial
Abstract
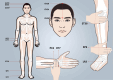
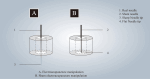
Background: Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a prevalent mental disorder characterized by excessive tension, worry, fear, and autonomic symptoms, which brings huge suffering to patients. Insomnia, one of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with GAD, often exacerbates anxiety symptoms. Electroacupuncture (EA), a non-pharmacological treatment for insomnia, presents several advantages, including significant efficacy, minimal side effects, and high patient acceptance. However, there is a lack of high-quality randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of EA.
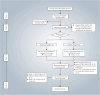
Methods: This study was designed as a randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial. 84 eligible patients with GAD-related insomnia will be randomly assigned to receive either three sessions of EA or sham EA weekly for 8 weeks. The primary outcome will be the change in the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) score at week 8. Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAMA), Insomnia Severity Index (ISI), sleep diary entries, actigraphy sleep assessment, 12-item Short-Form Health Survey, and weekly usage of medication will provide a thorough evaluation of sleep, anxiety, and overall living conditions.
Discussion: This study aims to evaluate the efficacy and safety of EA for treating insomnia in patients with GAD, proving EA can enhance patients' quality of life and reduce their dependence on medications.
Clinical trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier ChiCTR2400083326.
Keywords: electroacupuncture; generalized anxiety disorder; insomnia; protocol; randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Wang, Liu, Liu, Fan, Yin and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could be interpreted as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Electroacupuncture on Insomnia in Patients With Depression: A Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jul 1;5(7):e2220563. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.20563. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35797047 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of acupuncture treatment for breast cancer-related insomnia: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial.Front Psychiatry. 2024 May 23;15:1301338. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1301338. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38846918 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture for treating insomnia in patients with cancer: a study protocol for a randomised pilot clinical trial.BMJ Open. 2017 Aug 11;7(8):e016269. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-016269. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28801421 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of electroacupuncture for insomnia in cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2025 Feb 10;16:1512052. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1512052. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39995786 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of acupuncture versus sham/placebo acupuncture for insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 Nov;41:101253. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101253. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 33186824
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. Washington, D.C: American Psychiatric Association; (2013). p. 947.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

