Development of one-step multiplex real-time PCR for the detection of CHV-1, CAdV-2, and CDV
- PMID: 40417353
- PMCID: PMC12098444
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1583769
Development of one-step multiplex real-time PCR for the detection of CHV-1, CAdV-2, and CDV
Abstract
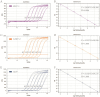
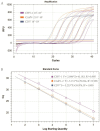
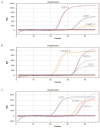
Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex (CIRDC) is a highly contagious disease that frequently affects canine populations and has emerged as a global epidemic. It has been reported that CIRDC can have a serious impact on related life. Therefore, the rapid detection and differentiation of common viruses that cause CIRDC are essential. It is generally believed that CIRDC is mainly caused by infection of three pathogens: canine herpesvirus-1 (CHV-1), canine adenovirus-2 (CAdV-2), and canine distemper virus (CDV). In this study, we developed and validated a TaqMan probe-based multiplex real-time PCR method to detect and identify these three viruses simultaneously. We designed specific primers and probes, and optimized the concentrations of each reactant in the system. The method was found to have good sensitivity, specificity and stability, and had a limit of detection of 102 copies/μL, 101 copies/μL and 101 copies/μL for CHV-1, CAdV-2, and CDV, respectively. In addition, co-infection simulation experiments confirmed that the method worked effectively, even if the concentrations of multiple viruses in the sample were close to the limit of detection or the concentrations of different viruses were different. The method was used to detect 122 clinical samples, and the results showed that it was more sensitive and reliable than conventional singleplex PCR. Thus, the method developed in this study is suitable for the clinical monitoring of CIRDC and is of great significance for the prevention and management of respiratory diseases in canine populations.
Keywords: CIRDC; canine adenovirus-2; canine distemper virus; canine herpesvirus-1; multiplex real-time PCR.
Copyright © 2025 Li, Wu, Wang, Jia, Yang, Lin, Ge and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid diagnosis of canine respiratory coronavirus, canine influenza virus, canine distemper virus and canine parainfluenza virus with a Taqman probe-based multiplex real-time PCR.J Virol Methods. 2024 Jul;328:114960. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2024.114960. Epub 2024 May 31. J Virol Methods. 2024. PMID: 38823586
-
Development of a three-panel multiplex real-time PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine canine respiratory pathogens.J Microbiol Methods. 2022 Aug;199:106528. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2022.106528. Epub 2022 Jun 23. J Microbiol Methods. 2022. PMID: 35753509
-
Development and application of multiplex PCR assays for detection of virus-induced respiratory disease complex in dogs.J Vet Med Sci. 2017 Jan 10;78(12):1847-1854. doi: 10.1292/jvms.16-0342. Epub 2016 Sep 15. J Vet Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 27628592 Free PMC article.
-
Aetiology of Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex and Prevalence of its Pathogens in Europe.J Comp Pathol. 2020 Apr;176:86-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2020.02.005. Epub 2020 Mar 17. J Comp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32359641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predominance of Canine Parainfluenza Virus and Mycoplasma in Canine Infectious Respiratory Disease Complex in Dogs.Pathogens. 2023 Nov 15;12(11):1356. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111356. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003820 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

