Automated multi-instance REDCap data synchronization for NIH clinical trial networks
- PMID: 40417400
- PMCID: PMC12103109
- DOI: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooaf036
Automated multi-instance REDCap data synchronization for NIH clinical trial networks
Abstract
Objectives: The main goal is to develop an automated process for connecting Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) instances in a clinical trial network to allow for deidentified transfer of research surveys to cloud computing data commons for discovery.
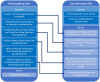
Materials and methods: To automate the process of consolidating data from remote clinical trial sites into 1 dataset at the coordinating/storage site, we developed a Hypertext Preprocessor script that operates in tandem with a server-side scheduling system (eg, Cron) to set up practical data extraction schedules for each remote site.
Results: The REDCap Application Programming Interface (API) Connection provides a novel implementation for automated synchronization between multiple REDCap instances across a distributed clinical trial network, enabling secure and efficient data transfer between study sites and coordination centers. Additionally, the protocol checker allows for automated reporting on conforming to planned data library protocols.
Discussion: Working from a shared and accepted core library of REDCap surveys was critical to the success of this implementation. This model also facilitates Institutional Review Board (IRB) approvals because the coordinating center can designate which surveys and data elements to be transferred. Hence, protected health information can be transformed or withheld depending on the permission given by the IRB at the coordinating center level. For the NIH HEAL clinical trial networks, this unified data collection works toward the goal of creating a deidentified dataset for transfer to a Gen3 data commons.
Conclusion: We established several simple and research-relevant tools, REDCAP API Connection and REDCAP Protocol Check, to support the emerging needs of clinical trial networks with increased data harmonization complexity.
Keywords: Application Programming Interface; REDCap; chronic pain; opioid use.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Use of research electronic data capture (REDCap) in a sequential multiple assignment randomized trial (SMART): a practical example of automating double randomization.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Jul 6;23(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-01986-6. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023. PMID: 37415099 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Use of research electronic data capture (REDCap) in a sequential multiple assignment randomized trial (SMART): A practical example of automating double randomization.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 24:rs.3.rs-2573133. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2573133/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: BMC Med Res Methodol. 2023 Jul 6;23(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12874-023-01986-6. PMID: 36865151 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A mobile app for delirium screening.JAMIA Open. 2021 May 20;4(2):ooab027. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooab027. eCollection 2021 Apr. JAMIA Open. 2021. PMID: 34549169 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Using a computerised database (REDCap) to monitor influenza vaccination coverage of healthcare workers and staff in South Eastern Sydney Local Health District.Aust Health Rev. 2021 Feb;45(1):97-103. doi: 10.1071/AH20006. Aust Health Rev. 2021. PMID: 32853535 Review.
References
Grants and funding
- R01 DA056045/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 DA055311/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA058620/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DA055306/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA058673/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DA057612/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 DA055301/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA058621/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DA058606/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA058694/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 DA055310/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RM1 DA055437/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA056537/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R25 DA061740/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
