Deep Learning-based Time-to-event Analysis of Depression and Asthma using the All of Us Research Program
- PMID: 40417537
- PMCID: PMC12099346
Deep Learning-based Time-to-event Analysis of Depression and Asthma using the All of Us Research Program
Abstract
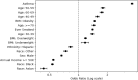
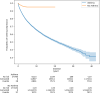
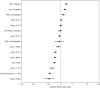
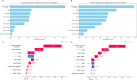
While there is a growing recognition of the association between depression and asthma, few studies have leveraged deep learning-based (DL-based) models in a retrospective cohort study with a large sample size. We analyzed the association between depression and asthma among 239,161 participants of the All of Us Research Program through DL-based, logistic regression, and Cox Proportional Hazards (CoxPH) models. We used SHAP values to help interpret DL-based models and c-index to evaluate model performance. Results suggest a significant odds ratio for depression in asthma. The c-indices for the CoxPH, DeepSurv, and DeepHit models were 0.619, 0.625, and 0.596, respectively. SHAP indicated a different set of important variables when compared with the CoxPH model. In conclusion, we provide strong evidence of a positive relationship between depression and asthma. Also, DL-based models did not outperform the CoxPH model on the c-index. Sex at birth and income may play important roles in occurrence of depression in asthma patients.
©2024 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deep learning models for predicting the survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results (SEER) database analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 9;14(1):13232. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63531-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38853169 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an individualized dementia risk prediction model using deep learning survival analysis incorporating genetic and environmental factors.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024 Dec 30;16(1):278. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01663-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 39736679 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a deep learning-based survival prediction model for pediatric glioma patients: A retrospective study using the SEER database and Chinese data.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Nov;182:109185. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.109185. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39341114
-
Development of a Spine X-Ray-Based Fracture Prediction Model Using a Deep Learning Algorithm.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022 Aug;37(4):674-683. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2022.1461. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2022. PMID: 35927066 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the performance of statistical, machine learning, and deep learning algorithms to predict time-to-event: A simulation study for conversion to mild cognitive impairment.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 22;19(1):e0297190. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297190. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38252622 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moorman JE, Rudd RA, Johnson CA, King M, Minor P, Bailey C, et al. National surveillance for asthma--United States, 1980-2004. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep Surveill Summ Wash DC 2002. 2007 Oct 19;56(8):1–54. - PubMed
-
- Tomassen P, Vandeplas G, Van Zele T, Cardell LO, Arebro J, Olze H, et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 May;137(5):1449–1456.e4. - PubMed
-
- Ding S, Zhong C. Exercise and Asthma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1228:369–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
