Global trends and hotspots in artificial intelligence for high myopia: a bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 40417679
- PMCID: PMC12098612
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1567440
Global trends and hotspots in artificial intelligence for high myopia: a bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to conduct a bibliometric analysis of global publications on the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in high myopia (HM).
Methods: We retrieved publications on AI in HM from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database, MEDLINE and Chinese Science Citation Database (CSCD) with data up to 2024. The analysis focused on publication and citation trends, identifying key articles, influential countries, institutions, authors, and journals. Additionally, we explored research domains and emerging keywords.
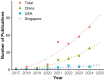
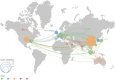
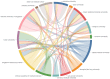
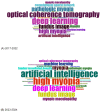
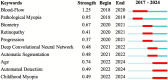
Results: A total of 167 relevant publications were included. The first AI-related paper on HM was published in 2017, with a significant surge in 2021, followed by a consistent increase in publication and citation counts over the next 3 years. China emerged as the most productive country, with the most extensive international collaboration. East Asian authors dominated the top 10 most influential authors. Yang, Weihua and Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science (IOVS) contributed the most publications among authors and institutions, respectively. Keyword analysis revealed that retinal imaging-related terms remained a consistent research focus, while newly emerging keywords included "automated detection" and "childhood."
Conclusion: Recent advancements in AI applications for HM have been significant and are expected to continue. Future research will likely focus on multimodal imaging and improving algorithm accessibility. Our findings offered the first comprehensive overview of global research on AI in HM, thus providing valuable insights for researchers to understand the current status and future trends in this field.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; bibliometric analysis; data visualization; global research; high myopia.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wumaier, Wang, Song, Cai, Han, Han and Fang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Research Trends in the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Oncology: A Bibliometric and Network Visualization Study.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022 Aug 31;27(9):254. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2709254. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2022. PMID: 36224012
-
The published role of artificial intelligence in drug discovery and development: a bibliometric and social network analysis from 1990 to 2023.J Cheminform. 2025 May 8;17(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13321-025-00988-4. J Cheminform. 2025. PMID: 40341055 Free PMC article.
-
Global research of artificial intelligence in strabismus: a bibliometric analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 20;10:1244007. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1244007. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37799591 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in Alzheimer's disease: a bibliometric analysis.Front Neurosci. 2025 Feb 14;19:1511350. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1511350. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40027465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global research trends and focus on immunotherapy for endometrial cancer: a comprehensive bibliometric insight and visualization analysis (2012-2024).Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 8;16:1571800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1571800. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40264788 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

