The role of FAPI PET/CT in patients with lymphoma: a systematic review
- PMID: 40417720
- PMCID: PMC12101064
- DOI: 10.3389/fnume.2025.1589903
The role of FAPI PET/CT in patients with lymphoma: a systematic review
Abstract
Introduction: Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT is typically the reference imaging method for assessing and tracking lymphomas. However, fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET is being explored as a potentially useful option, especially when Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) scans do not show clear results.
Methods: For this systematic review, two researchers searched PubMed/MEDLINE and Cochrane CENTRAL for studies on FAPI PET/CT in lymphoma patients.
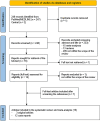
Results: The literature search initially retrieved 249 articles. After removing duplicates and screening titles and abstracts, and full text, there was a final selection of 15 articles (3 original studies and 12 case reports), encompassing a total of 270 patients. The three original studies were judged to have a low risk of bias according to the QUADAS-2 criteria. The systematic review reveals that FAPI PET/CT exhibits lower diagnostic sensitivity than [18F]FDG PET/CT in lymphomas characterized by low FAP expression. Nevertheless, FAPI PET/CT retains potential as a complementary imaging modality.
Discussion: [18F]FDG PET/CT remains the gold standard in lymphoma imaging, but FAPI PET/CT can potentially provide supplementary information regarding the molecular characteristics of lymphomas. FAPI PET/CT may have prognostic and therapeutic implications. In particular, it could help identify lymphoma subgroups with distinct stromal environments, potentially serving as a prognostic biomarker. Further large-scale prospective studies are warranted to validate its role in lymphoma management.
Keywords: DLBCL; FAPI; FDG; NHL; lymphoma; positron emission tomography; systematic review.
© 2025 Quartuccio, Nicolosi, Pulizzi, D’Oppido and Ialuna.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Hell J Nucl Med. 2023 May-Aug;26(2):123-131. doi: 10.1967/s002449912575. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Hell J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37527048
-
Performance of [18F]FDG PET/CT versus FAPI PET/CT for lung cancer assessment: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2024 Feb;34(2):1077-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10013-7. Epub 2023 Aug 17. Eur Radiol. 2024. PMID: 37589901
-
Predictive performance of [18F]F-fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-42 positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) in evaluating response of recurrent or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: complementary or alternative to [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET/CT?Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Aug 1;14(8):5333-5345. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-192. Epub 2024 Jun 21. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 39144061 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of FAPI PET/CT in Oncologic Studies: Systematic Review and Metaanalysis.J Nucl Med. 2023 Aug;64(8):1218-1224. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.265471. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Nucl Med. 2023. PMID: 37290798
-
Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy between 18F-FAPI-04 PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the clinical stage IA of lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Feb 28;17(2):661-675. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1658. Epub 2025 Feb 27. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40083505 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous