Polybenzimidazole Aerogels with High Thermal Stability and Mechanical Performance for Advanced Thermal Insulation Applications
- PMID: 40417788
- PMCID: PMC12147065
- DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5c05737
Polybenzimidazole Aerogels with High Thermal Stability and Mechanical Performance for Advanced Thermal Insulation Applications
Abstract
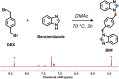
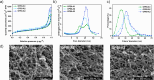
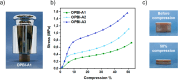
Advancements in the development of high-performance organic aerogels are essential for cutting-edge thermal insulation applications, where lightweight and durable structures, low thermal conductivity, and exceptional thermal stability are critical requirements. In this work, we present thermally stable and mechanically robust organic aerogels based on cross-linked benzimidazole-rich structures, specifically designed for thermal insulation. These aerogels exhibit a combination of valuable properties, including low density, large specific surface area and high porosity. Their tortuous mesoporous structures effectively reduce heat transfer by limiting gas-phase conduction, resulting in thermal conductivities as low as 23.9 mW m-1 K-1. This is coupled with a remarkable resistance to thermal decomposition (Td1% > 500 °C), surpassing the stability of the original polymer precursor (OPBI). Additionally, the strong polymer network, reinforced by both covalent and noncovalent interactions, provides exceptional mechanical strength, allowing the aerogels to withstand substantial loads without fracturing. This unique combination of low density, high porosity, robust mechanical performance, and superior thermal stability makes these aerogels highly promising for demanding thermal insulation applications, such as thermal protection for space exploration vehicles, fire-resistant suits, and EV battery insulation.
Keywords: aerogels; insulation; polybenzimidazole; thermal insulation; thermal stability.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mechanically Strong and Thermally Stable Chemical Cross-Linked Polyimide Aerogels for Thermal Insulator.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022 Nov 9;14(44):50129-50141. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c14007. Epub 2022 Oct 29. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022. PMID: 36308398
-
Nacre-Mimetic Nanocomposite Aerogels with Exceptional Mechanical Performance for Thermal Superinsulation at Extreme Conditions.Adv Mater. 2023 Jul;35(29):e2300813. doi: 10.1002/adma.202300813. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 37080594
-
Characteristics of Polybenzoxazine Aerogels as Thermal Insulation and Flame-Retardant Materials.Gels. 2025 Feb 6;11(2):121. doi: 10.3390/gels11020121. Gels. 2025. PMID: 39996664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultralight and Flexible Subnanowire Aerogels for Intrinsically Hydrophobic Thermal Insulation.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025 Jan 29;17(4):6815-6824. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c20157. Epub 2025 Jan 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2025. PMID: 39817330
-
Elastic SiC Aerogel for Thermal Insulation: A Systematic Review.Small. 2024 Aug;20(32):e2311464. doi: 10.1002/smll.202311464. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Small. 2024. PMID: 38511588 Review.
References
-
- Aegerter, M. ; Leventis, N. ; Koebel, M. ; Steiner, S. . Springer Handbook of Aerogels; Springer, 2023.
-
- Maleki H., Hüsing N.. Current Status, Opportunities, and Challenges in Catalytic and Photocatalytic Applications of Aerogels: Environmental Protection Aspects. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;221:530. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.012. - DOI
-
- Keshavarz L., Ghaani M., MacElroy J. D., English N.. A Comprehensive Review on the Application of Aerogels in CO2-Adsorption: Materials and Characterisation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;412:128604. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128604. - DOI
-
- Xiao Y., Yan M., Shi L., Gong L., Cheng X., Zhang H., Pan Y.. High-Temperature Resistant, Super Elastic Aerogel Sheet Prepared Based on In-Situ Supercritical Separation Method for Thermal Runaway Prohibition of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2023;61:102871. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2023.102871. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

