Interleukin-1 Signaling on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Accelerates Atherosclerosis in a Murine Model of Kawasaki Disease
- PMID: 40417796
- PMCID: PMC12229219
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.124.040687
Interleukin-1 Signaling on Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Accelerates Atherosclerosis in a Murine Model of Kawasaki Disease
Abstract
Background: We previously showed that Lactobacillus casei cell wall extract-induced Kawasaki disease (KD) vasculitis significantly accelerates atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice on high-fat diet. Here, we investigated the contribution of IL-1 (interleukin-1) signaling on vascular smooth muscle cells in this model.
Methods: Tamoxifen-inducible vascular smooth muscle cell-specific IL-1 receptor (Il1r1) knockout (SMCΔ/Δ) mice and Il1r1SMCWT/WT [wildtype/wildtype] littermate controls, all on ApoE-/- background, were injected with either PBS or Lactobacillus casei cell wall extract. Two weeks later, mice were fed a tamoxifen diet for 2 weeks to induce Il1r1 deletion on vascular smooth muscle cells before being exposed to 8 weeks of Western diet to promote atherosclerosis.
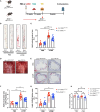
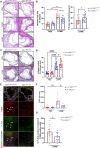
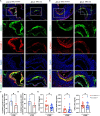
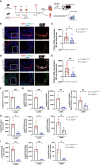
Results: KD vasculitis led to a significant acceleration of atherosclerosis. Il1r1SMCΔ/Δ mice had significantly diminished atherosclerotic plaque size, macrophage infiltration, and necrotic core formation in the aortic root, as well as diminished lipid accumulation in the aorta en face compared with control mice, despite similar serum cholesterol levels. Il1r1SMCΔ/Δ mice also had significantly diminished expression of endothelial adhesion molecules VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1) and ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) in the lesion area, as well as reduced serum MCP-1 (monocyte chemotaxis protein-1) levels compared with Il1r1SMCWT/WT control mice. Monocyte and macrophage recruitment was significantly reduced in the Il1r1SMCΔ/Δ group compared with the Il1r1SMCWT/WT group.
Conclusions: Our results suggest an important pathophysiologic link between IL-1 signaling on vascular smooth muscle cells and subsequent acceleration of atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic mice following KD vasculitis. Thus, further studies are warranted to investigate the role of IL-1 signaling not only in acute KD but also in the subsequent vascular remodeling and long-term complications of KD vasculitis, including accelerated atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Kawasaki disease; atherosclerosis; interleukin‐1; vascular smooth muscle cell; vasculitis.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA, Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P, Baltimore RS, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long‐term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis and Kawasaki disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation. 2004;110:2747–2771. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000145143.19711.78 - DOI - PubMed
-
- McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M, Shah PB, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long‐term management of Kawasaki disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135:e927–e999. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000484 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Orenstein JM, Shulman ST, Fox LM, Baker SC, Takahashi M, Bhatti TR, Russo PA, Mierau GW, de Chadarévian JP, Perlman EJ, et al. Three linked vasculopathic processes characterize Kawasaki disease: a light and transmission electron microscopic study. PLoS One. 2012;7:e38998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038998 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

