Immediate breast reconstruction surgery for breast cancer: current status and future directions
- PMID: 40418512
- PMCID: PMC12174185
- DOI: 10.1007/s12282-025-01723-5
Immediate breast reconstruction surgery for breast cancer: current status and future directions
Abstract
Background: Immediate breast reconstruction (IBR) has become increasingly recognized in Japan as an important component of breast cancer care, improving patients' quality of life after mastectomy. While the adoption of IBR is growing, the reconstruction rate in Japan remains lower than in Western countries. To clarify the current practice and challenges, the Japanese Breast Cancer Society (JBCS) conducted a nationwide survey.
Methods: We conducted a comprehensive web-based questionnaire survey among all JBCS-certified institutions between December 2020 and February 2021. The survey assessed institutional capabilities, surgical techniques, decision-making criteria for BR, and the integration of adjuvant therapy.
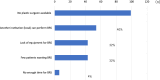
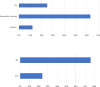
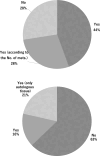
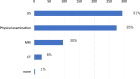
Results: A total of 429 institutions responded, with 72.5% offering BR and 61.7% capable of providing immediate reconstruction. Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) was performed at 73.7% of institutions offering reconstruction. Multidisciplinary conferences with plastic surgeons were held at 70.5% of institutions. Approximately 30% of institutions discontinued IBR if sentinel lymph node metastases were detected intraoperatively, and 62.8% avoided recommending IBR for patients likely to require postoperative radiation therapy. In 94% of institutions, BR did not cause delays in the administration of adjuvant chemotherapy. However, 15% of institutions modified their radiation therapy approach in reconstructed patients. Additionally, 27% of physicians still believed that BR could negatively affect prognosis.
Conclusions: The survey confirmed that IBR is widely performed and feasible in Japan. However, institutional differences, limited access to plastic surgeons, and persistent misconceptions remain significant barriers. Strengthening multidisciplinary collaboration and establishing standardized guidelines will help improve BR rates and patient outcomes in Japan.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Complications; Immediate reconstruction surgery; Prognosis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Tadahiko Shien reported the personal speaker fee from Allergan Aesthetics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mastectomy Alone or with Immediate Breast Reconstruction: Trend, Precipitating Factors, Patients Reported Outcome, and Oncologic Safety Analysis with and without Propensity Score Matching from 3759 Mastectomy Patients.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jul;49(13):3715-3727. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-04762-7. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40050543 Free PMC article.
-
Changing practice patterns in axillary management for patients with node-positive breast cancer towards increased use of sentinel lymph node biopsy-alone after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results of a survey (MF17-01) among Turkish surgeons.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2025 Jun 16;410(1):196. doi: 10.1007/s00423-025-03767-9. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2025. PMID: 40522373 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-operative radiotherapy for breast cancer patients receiving mastectomy and immediate autologous tissue reconstruction.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025 Aug;51(8):110110. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2025.110110. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40347716
-
Performance of sentinel lymph node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in clinically node-positive breast cancer patients: systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2025 Apr 1;111(4):3040-3050. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000002275. Int J Surg. 2025. PMID: 39878175 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal administration of progestogens for preventing spontaneous preterm birth in women with a multiple pregnancy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 20;2019(11):CD012024. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012024.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31745984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sasada S, Nagura N, Shimo A, et al. Impact of radiation therapy for breast cancer with involved surgical margin after immediate breast reconstruction: A multi-institutional observational study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2024;50(6):108360. - PubMed
-
- Shiraishi M, Sowa Y, Inafuku N. Long-term survey of sexual well-being after breast reconstruction using the BREAST-Q in the Japanese population. Asian J Surg. 2023;46(1):150–5. - PubMed
-
- Ogiya A, Nagura N, Shimo A, et al. Long-term outcomes of breast cancer patients with local recurrence after mastectomy undergoing immediate breast reconstruction: a retrospective multi-institutional study of 4153 cases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023;30(11):6532–40. - PubMed
-
- Seki H, Ogiya A, Nagura N, et al. Prognosis of isolated locoregional recurrence after early breast cancer with immediate breast reconstruction surgery: a retrospective multi-institutional study. Breast Cancer. 2024;31(5):935–44. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

