A new perspective in avian bone health: dietary supplementation with a standardized dry grape extract improves pullets' bones' quality through metabolic modulation
- PMID: 40418877
- PMCID: PMC12159908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105270
A new perspective in avian bone health: dietary supplementation with a standardized dry grape extract improves pullets' bones' quality through metabolic modulation
Abstract
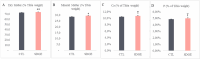
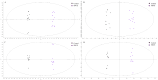
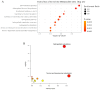
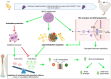
In laying hens, maintaining optimal bone health and development from the early stages is crucial, as it directly affects their egg-laying efficiency, overall welfare and productivity. Studies have shown that grape polyphenols from Vitis vinifera enhance bone health in both humans and animals. Still, the mechanisms behind this effect remain unclear, given the diversity of grape polyphenols and their varying mechanisms of action. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of a standardized dry grape extract (SDGE) on bone quality and metabolome of future laying hens reared in commercial conditions. Therefore, 36300 day-old pullets were randomly divided into two barns on the same farm site. Both received the same diet, with the addition of 30 mg/kg of SDGE (Nor-Grape®, Nor-Feed, France) from day 1 until week 17 in the supplemented group (SDGE). At the end of the supplementation period, several bone quality parameters were analyzed on 50 individuals per group. Additionally, non-targeted metabolomics on plasma and bones were performed to uncover the impact of SDGE supplementation on pullet's metabolome. Results demonstrated that keel bone deformity tended to improve following SDGE supplementation (P = 0.10). Moreover, SDGE intake significantly increased bone dry and mineral content, compared to the control group (P < 0.05) and tended to increase calcium (Ca) (P = 0.074) and phosphorus (P) content (P = 0.055). On the other hand, non-targeted metabolomics on plasma samples revealed an impact on fatty acids and glycerophospholipid metabolisms while bone samples analysis uncovered pathways related to sphingolipid and estrogen mediated signaling pathways. Overall, this study suggests novel mechanisms related to estrogen signaling through lipid metabolism in SDGE supplemented pullets and highlights that nutritional intervention with SDGE in early developmental stage of future laying hens improves their bone health prior to entry into the laying phase, thus proving a useful tool in bone health management.
Keywords: Standardized dry grape extract; bone strength; laying hen; metabolomics.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: ABERKANE Fatima Zohra reports equipment, drugs, or supplies was provided by NOR-FEED. Aberkane Fatima Zohra reports a relationship with NOR-FEED that includes: employment. Paul Engler reports a relationship with NOR-FEED that includes: employment. Mohamed El Amine BENARBIA reports a relationship with NOR-FEED that includes: employment. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Guanidinoacetic acid in laying hen diets with varying dietary energy: Productivity, antioxidant status, yolk fatty acid profile, hepatic lipid metabolism, and gut health.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105159. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105159. Epub 2025 Apr 13. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40267570 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Feed for Laying Hens: Application of Saffron Extract as Eco-Friendly Supplement With Cholesterol-Lowering Properties.Vet Med Sci. 2025 Jan;11(1):e70155. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70155. Vet Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39642059 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Bacillus subtilis ZY1 on production performance, egg quality, serum parameters and intestinal health in laying hens.Poult Sci. 2025 Jul;104(7):105120. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105120. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40319583 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Almeida Mallmann B., Martin E.M., Soo Kim K., Calderon-Apodaca N.L., Baxter M.F.A., Latorre J.D., Hernandez-Velasco X., Paasch-Martinez L., Owens C.M., Dridi S., Bottje W.G., Greene E.S., Tellez-Isaias G. Evaluation of bone marrow adipose tissue and bone mineralization on broiler chickens affected by wooden breast myopathy. Front. Physiol. 2019;10 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00674. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/physiology/articles/10.3389/fphys.2... Available from: - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

