[Treatment strategy for severe radiation-induced ulcers near major blood vessels]
- PMID: 40419356
- PMCID: PMC12123596
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240521-00191
[Treatment strategy for severe radiation-induced ulcers near major blood vessels]
Abstract
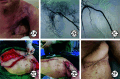
Objective: To investigate the treatment strategy for severe radiation-induced ulcers near major blood vessels. Methods: This study was a retrospective observational study. From January 2016 to December 2023, 23 patients with radiation-induced ulcers near major blood vessels who met the inclusion criteria were admitted to Beijing Jishuitan Hospital of Capital Medical University, including 18 females and 5 males, aged 39 to 77 years. Ulcers were distributed in the axilla in 11 cases, in the groin in 4 cases, in the neck in 5 cases, and in the subclavicular region in 3 cases. According to the distance between the ulcer base and the major blood vessels, the ulcers were classified. The ulcers with major blood vessels exposed at the ulcer base was classified as exposed-vessel type (2 cases), the distance between the ulcer base and the major blood vessel wall ≤1 cm was classified as near-vessel type (8 cases), and the distance between the ulcer base and the major blood vessel wall >1 cm was classified as distant-vessel type (13 cases). After comprehensive preoperative evaluation and multidisciplinary team collaboration, the covered stents were implanted before surgery in patients with exposed-vessel type of ulcers and partial patients with near-vessel type of ulcers and high risk of vascular rupture, while preoperative vascular localization and careful operation were conducted during surgery to prevent vascular injury in other patients. After radical debridement, the wounds were repaired with flaps or myocutaneous flaps, the wound area after debridement was 6 cm×5 cm to 22 cm×12 cm, and the area of the flaps or myocutaneous flaps was 14 cm×9 cm to 27 cm×10 cm. The classification of ulcers in different regions, specific wound repair methods, and bacterial culture results of wound tissue specimens collected during the surgery were recorded. The survivals of flaps or myocutaneous flaps after surgery, the recurrence of infection or sinus, and wound healing were observed during follow-up after surgery. Results: Among the 11 patients with axillary ulcers, 3 had near-vessel type of ulcers, 8 had distant-vessel type of ulcers; among the 3 patients with subclavicular ulcers, one had near-vessel type of ulcer and two had distant-vessel type of ulcers, which were repaired with rectus abdominis myocutaneous flaps or latissimus dorsi myocutaneous flaps. Among the 5 patients with neck ulcers, two had exposed-vessel type of ulcers, and 3 had near-vessel type of ulcers, which were repaired with pectoralis major myocutaneous flaps or transverse carotid artery perforator flaps. Among the 4 patients with groin ulcers, one had near-vessel type of ulcer, and 3 had distant-vessel type of ulcers, which were repaired with tensor fascia lata myocutaneous flaps, anterolateral thigh flaps, or contralateral rectus abdominis myocutaneous flaps. The bacteria detected in the wound tissue specimens collected during surgery were mainly Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus capitis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Follow-up for 1 to 25 months after surgery showed that the flaps or myocutaneous flaps survived well in 14 patients and the wounds healed; two patients with infection at the flap edge healed after dressing change; seven patients had unhealed wounds due to infection recurrence or partial necrosis of the flaps. Among them, five patients underwent perforator flap or local flap transplantation again to repair the wounds, and two patients had wound healing after debridement and suture. Three patients who underwent stent implantation had their wounds healed without recurrence of infection or sinus. Conclusions: A distance-based classification for ulcers between the major blood vessels and the ulcer base, selective covered stent implantation, multidisciplinary team collaboration, and radical debridement enable safe reconstruction of radiation-induced ulcers near major vessels, significantly reducing vascular injury and infection recurrence risks.
目的: 探讨大血管部位严重放射性溃疡的治疗策略。 方法: 该研究为回顾性观察性研究。2016年1月—2023年12月,首都医科大学附属北京积水潭医院收治23例符合入选标准的放射性溃疡患者且溃疡靠近大血管,其中女18例、男5例,年龄39~77岁。溃疡分布于腋部者11例、腹股沟区域者4例、颈部者5例、锁骨下区域者3例。根据溃疡基底与大血管之间的距离,进行溃疡分型,大血管暴露于溃疡基底为血管裸露型(2例),溃疡基底与大血管壁的距离≤1 cm为近血管型(8例),溃疡基底与大血管壁的距离>1 cm为远血管型(13例)。经过全面的术前评估、多学科团队合作,血管裸露型和部分血管破裂风险较大的近血管型溃疡者术前放置覆膜支架,其余患者通过术前血管定位及术中谨慎操作避免损伤血管。彻底清创后采用皮瓣或肌皮瓣修复创面,清创后创面面积为6 cm×5 cm~22 cm×12 cm,皮瓣或肌皮瓣面积为14 cm×9 cm~27 cm×10 cm。记录不同部位溃疡的分型情况、具体的创面修复方式、术中创面组织标本细菌培养结果。术后随访观察皮瓣或肌皮瓣存活情况、感染或窦道复发情况及创面愈合情况。 结果: 11例腋部溃疡患者中溃疡为近血管型者3例、远血管型者8例,3例锁骨下溃疡患者中溃疡为近血管型者1例、远血管型者2例,采用腹直肌肌皮瓣或背阔肌肌皮瓣修复;5例颈部溃疡患者中溃疡为血管裸露型者2例、近血管型者3例,采用胸大肌肌皮瓣或颈横动脉穿支皮瓣修复;4例腹股沟溃疡患者中溃疡为近血管型者1例、远血管型者3例,采用阔筋膜张肌肌皮瓣、股前外侧皮瓣或对侧腹直肌肌皮瓣修复。术中取的创面组织标本中检出细菌主要为金黄色葡萄球菌、头状葡萄球菌、铜绿假单胞菌。术后随访1~25个月,14例患者皮瓣或肌皮瓣存活良好且创面愈合;2例患者皮瓣边缘感染经换药后愈合;7例患者因感染复发或皮瓣部分坏死致创面未愈合,其中5例患者再次行穿支皮瓣或局部皮瓣移植修复创面,2例患者创面经清创缝合后愈合。3例行支架植入术的患者创面均愈合,无感染或窦道复发。 结论: 基于大血管和溃疡基底距离的溃疡分型策略及选择性覆膜支架植入,结合多学科团队协作与彻底清创,可安全实现大血管部位严重放射性溃疡的修复,显著降低血管损伤与感染复发风险。.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- 沈 余明, 胡 云刚. 慢性放射性溃疡的诊疗策略. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志. 2024;40(6):501–506. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240308-00091. [沈余明, 胡云刚. 慢性放射性溃疡的诊疗策略[J]. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志, 2024, 40(6): 501-506. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240308-00091.] - DOI
-
- 夏 成德, 杨 阳. 放射性皮肤溃疡的治疗和预防策略. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志. 2024;40(8):719–724. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240415-00134. [夏成德, 杨阳. 放射性皮肤溃疡的治疗和预防策略[J]. 中华烧伤与创面修复杂志, 2024, 40(8): 719-724. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20240415-00134.] - DOI
-
- Hu Y, Yu L, Du W, et al. Global hotspots and research trends of radiation-induced skin injury: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023. Front Oncol. 2024;14:1430802. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1430802. [Hu Y, Yu L, Du W, et al. Global hotspots and research trends of radiation-induced skin injury: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1430802. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1430802.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kameni LE, Januszyk M, Berry CE, et al. A review of radiation-induced vascular injury and clinical impact. Ann Plast Surg. 2024;92(2):181–185. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003723. [Kameni LE, Januszyk M, Berry CE, et al. A review of radiation-induced vascular injury and clinical impact[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2024, 92(2): 181-185. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003723.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- 沈 余明, 沈 祖尧, 王 乃佐, et al. 严重放射性溃疡的修复. 中国修复重建外科杂志. 2000;14(4):208–210. [沈余明, 沈祖尧, 王乃佐, 等. 严重放射性溃疡的修复[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2000, 14(4): 208-210.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
