The small molecule drug CBL0137 interferes with DNA damage repair and enhances the sensitivity of NK/T-Cell lymphoma to cisplatin
- PMID: 40419449
- PMCID: PMC12118381
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2025.2511301
The small molecule drug CBL0137 interferes with DNA damage repair and enhances the sensitivity of NK/T-Cell lymphoma to cisplatin
Abstract
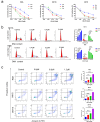
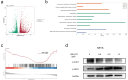
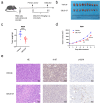
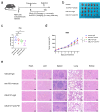
This study aimed to investigate the in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects and mechanisms of the small molecule anticancer drug CBL0137 in NK/T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL), as well as its efficacy when combined with chemotherapy or immunotherapy. Cell viability assays were performed to evaluate the inhibitory effect of CBL0137 on NKTCL cell proliferation in vitro. Flow cytometry was used to assess the effects of the drug on apoptosis and cell cycle progression. RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) was employed to explore the mechanism of action of CBL0137 in NKTCL, and Western blotting (WB) was used to validate the expression of related proteins. An in vivo xenograft model was used to confirm the antitumor activity of CBL0137. Additionally, immunohistochemistry analysis was conducted to further study tumor tissue. CBL0137 effectively inhibited the proliferation of NKTCL cells in vitro, induced apoptosis, and significantly blocked cell cycle progression. RNA-seq analysis revealed that CBL0137 exerts its antitumor effect primarily by interfering with DNA damage repair. In vivo experiments using xenografted mice confirmed the antitumor activity of CBL0137. CBL0137, when combined with PD-1 antibody, exhibits synergistic antitumor effects in mice, and its combination with cisplatin significantly enhances the sensitivity of NKTCL to cisplatin. CBL0137 inhibits DNA damage repair in NK/T-cell lymphoma and enhances its sensitivity to cisplatin.
Keywords: CBL0137; DNA damage repair; NK/T-cell lymphoma; PD-1 blockade; cancer therapy; cisplatin; mouse studies.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-2-inducible T-cell kinase inhibition to block NF-κB signaling exerts anti-tumor effects and enhances chemotherapy in NK/T-cell lymphoma.Cancer Lett. 2025 May 28;618:217602. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2025.217602. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 40054659
-
m6A methyltransferase Wilms' tumor 1-associated protein facilitates cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance in NK/T cell lymphoma by regulating dual-specificity phosphatases 6 expression via m6A RNA methylation.IUBMB Life. 2021 Jan;73(1):108-117. doi: 10.1002/iub.2410. Epub 2020 Nov 17. IUBMB Life. 2021. PMID: 33205540
-
A novel anti-CD47 antibody with therapeutic potential for NK/T-cell lymphoma.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2408088. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2408088. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39348228 Free PMC article.
-
PARP inhibitor exerts an anti-tumor effect via LMO2 and synergizes with cisplatin in natural killer/T cell lymphoma.BMC Med. 2023 Jul 13;21(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02904-9. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37442994 Free PMC article.
-
FACT inhibitor CBL0137, administered in an optimized schedule, potentiates radiation therapy for glioblastoma by suppressing DNA damage repair.J Neurooncol. 2024 Dec;170(3):621-630. doi: 10.1007/s11060-024-04819-8. Epub 2024 Sep 9. J Neurooncol. 2024. PMID: 39251545
References
-
- Perry AM, Diebold J, Nathwani BN, MacLennan KA, Muller-Hermelink HK, Bast M, Boilesen E, Armitage JO, Weisenburger DD. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the developing world: review of 4539 cases from the international non-Hodgkin lymphoma classification project. Haematologica. 2016;101(10):1244–1250. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.148809. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
