Association of circulating levels of anti-CarP antibodies with disease activity, disability and radiological damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients: an open-label, observational study
- PMID: 40419667
- PMCID: PMC12106665
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03464-z
Association of circulating levels of anti-CarP antibodies with disease activity, disability and radiological damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients: an open-label, observational study
Abstract
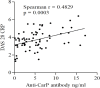
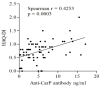
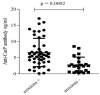
Autoantibodies directed against carbamylated proteins (anti-CarP) have been recently identified as predictors for RA development. The aim of this study was to determine the positivity of anti-CarP antibodies in a real-life cohort of RA patients and their association with radiological damage, disability and disease activity. In this open-label, observational, cross-sectional study 69 RA patients and 16 healthy controls (HC) were recruited. The study was approved by institutional Ethical Committee. Circulating levels of anti-CarP antibodies were determined by commercial ELISA anti-CarP quantitative sandwich immunoassay. Articular X-rays were evaluated to define the presence of bone erosions. Disease activity (DAS28-CRP) and disability (HAQ-DI) were assessed. Pearson χ2 test, Wilcoxon test or Kruskall-Wallis test was used. Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient was applied for continuous variables. Multivariable logistic regression model was performed. Anti-CarP positivity was found in 35% of RA patients and in no HC. One quarter of seronegative RA patients were anti-CarP positive. A positive correlation between levels of anti-CarP antibodies with DAS28-CRP (p = 0.0003; Spearman r = 0.4829) and HAQ-DI (p = 0.0003; Spearman r = 0.4253) was found. 87% of anti-CarP positive patients had erosions. At multivariable logistic regression analysis, RA disease activity (OR 1.31, 95% CI [1.14, 1.63]) and circulating levels of anti-CarP antibodies (OR 1.66, 95% CI [1.28, 2.37]) were independent predictors of bone erosions. Our study confirms that anti-CarP antibodies are associated with a more aggressive RA course and are independent predictors of bone erosions.
Keywords: Anti-CarP antibodies; Autoantibodies; Biomarkers; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of anti-citrullinated and anti-carbamylated antibodies in mexicans with rheumatoid arthritis and at-risk individuals.Rev Invest Clin. 2025 Jan 20;76(6):243-252. doi: 10.24875/RIC.24000181. Rev Invest Clin. 2025. PMID: 39836925
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Scott, D. L., Wolfe, F. & Huizinga, T. W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet376, 1094–1108 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Conigliaro, P. et al. Autoantibodies in inflammatory arthritis. Autoimmun Rev.15(7), 673–683 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Wynckel, A. et al. Kinetics of carbamylated haemoglobin in acute renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant.15, 1183–1188 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

