Base editing of trinucleotide repeats that cause Huntington's disease and Friedreich's ataxia reduces somatic repeat expansions in patient cells and in mice
- PMID: 40419681
- PMCID: PMC12165863
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-025-02172-8
Base editing of trinucleotide repeats that cause Huntington's disease and Friedreich's ataxia reduces somatic repeat expansions in patient cells and in mice
Abstract
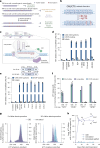
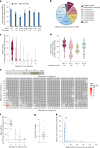
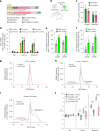
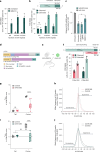
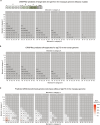
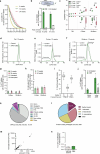
Trinucleotide repeat (TNR) diseases are neurological disorders caused by expanded genomic TNRs that become unstable in a length-dependent manner. The CAG•CTG sequence is found in approximately one-third of pathogenic TNR loci, including the HTT gene that causes Huntington's disease. Friedreich's ataxia, the most prevalent hereditary ataxia, results from GAA repeat expansion at the FXN gene. Here we used cytosine and adenine base editing to reduce the repetitiveness of TNRs in patient cells and in mice. Base editors introduced G•C>A•T and A•T>G•C interruptions at CAG and GAA repeats, mimicking stable, nonpathogenic alleles that naturally occur in people. AAV9 delivery of optimized base editors in Htt.Q111 Huntington's disease and YG8s Friedreich's ataxia mice resulted in efficient editing in transduced tissues, and significantly reduced repeat expansion in the central nervous system. These findings demonstrate that introducing interruptions in pathogenic TNRs can mitigate a key neurological feature of TNR diseases in vivo.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Z.M., M.A. and D.R.L. have filed patent applications on this work. D.R.L. is a consultant, co-founder and/or equity owner of Beam Therapeutics, Prime Medicine, Pairwise Plants and nChroma Bio, companies that use or deliver genome or epigenome editing agents. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Ramakrishnan, S., Shah, M. & Gupta, V. Trinucleotid Repeat Disorders. In StatPearls [Internet] (StatPearls Publishing, updated 11 December 2024).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

