Sustainable uric acid sensor based on a lab-fabricated electrode modified with rice straw-derived carbon materials
- PMID: 40419700
- PMCID: PMC12106630
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03405-w
Sustainable uric acid sensor based on a lab-fabricated electrode modified with rice straw-derived carbon materials
Abstract
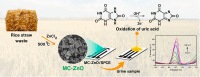
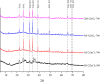
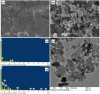
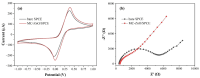
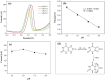
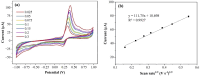
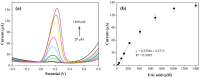
A novel and facile electrochemical sensor for the quantification of uric acid has been fabricated through the strategic modification of a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) using mesoporous carbon-zinc oxide (MC-ZnO) synthesized from rice straw waste. The MC-ZnO materials, generated via a controlled pyrolysis process, exhibit homogeneous dispersion and a substantial electroactive surface area of 0.1286 cm2. The electrochemical oxidation of uric acid exhibits a distinct peak at 0.18 V in differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), indicative of efficient charge transfer kinetics. A linear range spanning 20 to 225 µM was obtained with a limit of detection (LOD) of 3.76 µM, signifying exceptional analytical sensitivity. Furthermore, the sensor demonstrates robust selectivity toward uric acid in the presence of typical interferents, underscoring its applicability for precise uric acid determination in complex biological matrices. The sensor's analytical performance was validated by quantifying uric acid in spiked urine samples, yielding recovery rates between 97.9% and 114.8% and relative standard deviations (RSD) below 4.92%, affirming its accuracy and precision. This platform heralds a promising avenue for clinical diagnostics, leveraging sustainable materials for uric acid detection.
Keywords: Agricultural waste; Biomass; Eco-friendly sensor; Modified electrode; Voltammetry.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A simple ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of gallic acid and uric acid in human urine and fruit juices based on zirconia-choline chloride-gold nanoparticles-modified carbon paste electrode.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Aug 30;114:30-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 29775856
-
Electrochemical Determination of Doxorubicin in the Presence of Dacarbazine Using MWCNTs/ZnO Nanocomposite Modified Disposable Screen-Printed Electrode.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 17;15(1):60. doi: 10.3390/bios15010060. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852111 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Pd Confined Mesoporous Carbon Hollow Nanospheres for the Sensitive Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid.Molecules. 2024 May 21;29(11):2427. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112427. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893303 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine and uric acid electrochemical sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with cubic Pd and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017 Jul 1;497:172-180. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2017.03.011. Epub 2017 Mar 2. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2017. PMID: 28284071
-
Electrochemical determination of uric acid in the presence of dopamine and riboflavin using a poly(resorcinol)-modified carbon nanotube sensor.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5822. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90235-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962184 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Svistounov, D. et al. Development of quantitative assay for simultaneous measurement of purine metabolites and creatinine in biobanked urine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest.82 (1), 37–49. 10.1080/00365513.2021.2015799 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Khan, M. I. et al. Portable electrophoresis Titration chip model for sensing of uric acid in urine and blood by moving reaction boundary. Sens. Actuators B. 286, 9–15. 10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.098 (2019).
-
- Chenthattil, R. et al. Validated electrochemical method for simultaneous resolution of tyrosine, uric acid, and ascorbic acid at polymer modified nano-composite paste electrode. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem.56 (4), 415–426. 10.3103/s1068375520040134 (2020).
-
- Richette, P. & Bardin, T. Gout. Lancet375 (9711), 318–328. 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60883-7 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Zhao, C., Jiao, Y., Hu, F. & &Yang, Y. Green synthesis of carbon Dots from pork and application as nanosensors for uric acid detection. Spectrochim Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc.190, 360–367. 10.1016/j.saa.2017.09.037 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

