Therapeutic Applications of Ketogenic Diets in Lipedema: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence
- PMID: 40419722
- PMCID: PMC12106162
- DOI: 10.1007/s13679-025-00642-y
Therapeutic Applications of Ketogenic Diets in Lipedema: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence
Abstract
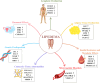
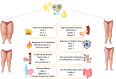
Purpose of review: Lipedema is an abnormal accumulation of adipose tissue, predominantly observed in women, characterised by symmetrical fat deposition and tactile sensitivity in the extremities, affecting both sides of the body. This condition can lead to significant pain, impairing daily activities and causing substantial discomfort.
Recent findings: While the etiology of the disease is not yet fully understood, genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, a stressful lifestyle, as well as traumatic events are considered potential triggers. Lipedema remains a condition with low diagnostic awareness as well as is frequently misdiagnosed as obesity or lymphedema. While obesity is a risk factor for lipedema, the abnormal fat deposition characteristic of the disease can occur across a wide spectrum of body weights, from underweight to overweight individuals. Specific patterns of adipose tissue distribution may be associated with signs of inflammation as well as heightened pain perception, as well as individuals with eating disorders, such as anorexia, may additionally be affected. Ketogenic diets have emerged as a promising therapeutic option for lipedema. Characterized by low carbohydrate as well as high fat content, ketogenic diets facilitate metabolic improvements by reducing insulin resistance as well as supporting weight loss. Furthermore, they may mitigate tissue damage associated with lipedema by decreasing inflammation as well as oxidative stress levels.Nevertheless, current scientific data regarding the mechanisms of action as well as therapeutic efficacy of ketogenic diets are limited, necessitating further research to expand their clinical application.
Keywords: Fat accumulation; Inflammation; Ketogenic diet; Ketosis; Lipedema.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics: The papers cited involving the use of human subjects, have been carried out in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for experiments involving humans. The papares cited involving animal research have been carried out in accordance with the U.K. Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act, 1986 and associated guidelines, EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments, or the National Institutes of Health guide for the care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No. 8023, revised 1978). Please note that in relation to the nature of the present manuscript (review), study registration/ethics committee approval is not required. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials