DRaCOon: a novel algorithm for pathway-level differential co-expression analysis in transcriptomics
- PMID: 40419963
- PMCID: PMC12107744
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-025-06162-9
DRaCOon: a novel algorithm for pathway-level differential co-expression analysis in transcriptomics
Abstract
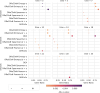
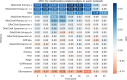
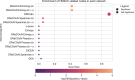
Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying diseases is crucial for more precise, personalized medicine. Pathway-level differential co-expression analysis, a powerful approach for transcriptomics, identifies condition-specific changes in gene-gene interaction networks, offering targeted insights. However, a key challenge is the lack of robust methods and benchmarks specifically for evaluating algorithms' ability to identify disrupted gene-gene associations across conditions. We introduce DRaCOoN (Differential Regulatory and Co-expression Networks), a Python package and web tool for pathway-level differential co-expression analysis. DRaCOoN uniquely integrates multiple association and differential metrics, with a novel, computationally efficient permutation test for significance assessment. Crucially, DRaCOoN also provides a benchmarking framework for comprehensive method evaluation. Extensive benchmarking on simulated data and three real-world datasets (bone healing, colorectal cancer, and head/neck carcinoma) showed that DRaCOoN, particularly with an entropy-based association measure and the s differential metric, consistently outperforms eight other methods. It remains highly accurate in balanced datasets, robust to varying gene perturbation levels, and identifies biologically relevant regulatory changes. Furthermore, DRaCOoN serves as both a powerful tool and a benchmarking framework for elucidating disease mechanisms from transcriptomics data, advancing precision medicine by uncovering critical gene regulatory alterations.
Keywords: Differential networking; Differential regulation; Disease module identification; Network-based gene expression analysis; Pathway-level differential co-expression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no Conflict of interest. Authors’ information: Not applicable.
Figures





References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

