Cytomegalovirus primo-infection in Guillain-Barré syndrome during pregnancy, a case report of a very serious and rare case
- PMID: 40420037
- PMCID: PMC12107956
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-025-04233-1
Cytomegalovirus primo-infection in Guillain-Barré syndrome during pregnancy, a case report of a very serious and rare case
Abstract
Background: Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) during pregnancy can be a very severe and life-threatening condition for both mother and child. GBS due to cytomegalovirus (CMV) in pregnancy is even rarer and may be associated with more respiratory insufficiency, cranial nerve involvement and sensory loss in the mother.
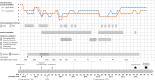
Case presentation: A 29-year-old secondparous woman at 25 weeks of gestation (WG) presented with a rapid ascending tetraparesis, bulbar paralysis, bilateral facial palsy, right-sided abducens paresis within 72 h of symptom onset and respiratory failure after 12 days. She needed intubation and mechanical ventilation for cumulative 42 days. GBS due to CMV primo-infection was diagnosed. A multidisciplinary team was involved to monitor and manage patient and fetus. In the electrodiagnostic studies, the patient presented severe primarily demyelinating features consistent with an acute inflammatory demyelinating (AIDP) GBS form treated with repeated plasma exchanges and administration of intravenous immunoglobulins. At 34 + 1 WG a cesarean delivery was performed, the newborn was healthy without intrauterine CMV-transmission.
Conclusion: The optimal time of delivery for intubated pregnant GBS patients is unknown. The mother's respiratory and medical conditions should be assessed in relation to premature-associated morbidity of the newborn.
Keywords: CMV; Cytomegalovirus; GBS; Guillain-Barré syndrome; Pregnancy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. The research project does not fall within the scope of the Human Research Act (HRA). Therefore, an authorization from the ethics committee was not required. Consent for publication: Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this Case report. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor of this journal. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cheng Q, Jiang GX, Fredrikson S, Link H, de Pedro-Cuesta J. Increased incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome postpartum. Epidemiology. 1998;9(6):601-4. PMID: 9799167. - PubMed
-
- Chan LY, Tsui MH, Leung TN. Guillain-Barré syndrome in pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2004;83(4):319–25. PMID: 15005776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical