The relationship between enamel and dentin calibrated-radiographic-density measured by cone beam computed tomography and dental caries status in young adults
- PMID: 40420104
- PMCID: PMC12107938
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-025-06146-4
The relationship between enamel and dentin calibrated-radiographic-density measured by cone beam computed tomography and dental caries status in young adults
Erratum in
-
Correction: The relationship between enamel and dentin calibrated-radiographic-density measured by cone beam computed tomography and dental caries status in young adults.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jun 28;25(1):960. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06411-6. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40581652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the relationship between caries experience measured by the decayed missing filled teeth (DMFT) index and the radiographic density of dental hard tissues measured by cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) with a novel calibration tool for individuals aged > 20 to 25 years.
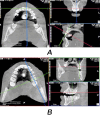
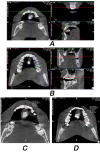
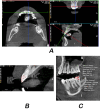
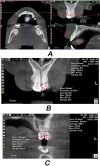
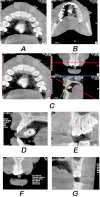
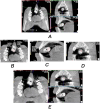
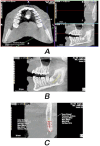
Materials and methods: The sample consisted of 40 patients. Their DMFT ranged from 1 to 16 (mean = 6.5, standard deviation = 3.4). CBCT was performed for all patients, and an extracted tooth covered with self-cured acrylic resin was used as a radiographic density calibration tool. The gray values of the enamel, coronal and radical dentine regions of all the teeth were measured by two examiners. The average values of enamel and dentine radiographic density of incisors, canines, premolars and molars in each jaw and both jaws were calculated, and correlated with DMFT.
Results: The radiographic density of mandibular incisors and all incisors of both jaws had the highest Pearson correlation coefficients with DMFT (0.33 < r < 0.42, P-value = 0.016). Neither the coronal nor the radicular dentine radiographic density was correlated with the DMFT according to any examiner.
Conclusion: Enamel, not dentine, radiographic density calculated from incisors via CBCT scans was correlated with DMFT in individuals aged > 20 to 25 years. The strengths of these correlations were moderate.
Clinical relevance: The enamel radiographic density of incisors, measured by CBCT using a novel calibration tool, was correlated with dental caries status in young adults aged 20-25 years. Thus, this study provides deeper insight into the radiographic density of dental hard tissues as a determinant of dental caries. This factor is also measurable in a clinical setting.
Keywords: Cone beam computed tomography; DMFT; Dental caries; Dentine; Enamel; Radiographic density.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval and consent to participate: Ethical approval was obtained from Al-Wataniya Private University- Faculty of Dentistry for performing this research (No. 711–2021), after reviewing the protocol by the appropriate institutional review board (IRB). All experiments on human subjects were conducted in accordance with The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) and that all procedures were carried out with the adequate understanding and written informed consent from all participated subjects. Consent for publication: Not Applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ruprecht A. Oral and maxillofacial radiology: then and now. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008;139(Suppl):S5–6. - PubMed
-
- Ritter AV. Sturdevant’s art & science of operative dentistry-e-book. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2017.
-
- SohrabiVafa M, Moeini B, Hazavehei MM, Soltanian A, Rezaei L. The effect of education based on health belief model (HBM) in decreasing dental plaque index among first grade of middle-school Girl students in Hamadan. J Urmia Nurs Midwifery Fac. 2013;11(8):639–48.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

