The effects of the mediterranean diet supplemented with olive oils on pro-inflammatory biomarkers and soluble adhesion molecules: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40420157
- PMCID: PMC12105412
- DOI: 10.1186/s12986-025-00947-8
The effects of the mediterranean diet supplemented with olive oils on pro-inflammatory biomarkers and soluble adhesion molecules: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Inflammation plays a pivotal role in Cardiovascular disease (CVD) which are a major global health burden. The oil-supplemented Mediterranean diet (MED) is associated with anti-inflammatory effects. The current study evaluates the impact of an olive oils-supplemented MED on pro-inflammatory biomarkers and soluble adhesion molecules.
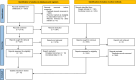
Methods: Regarding PRISMA guideline, this study was conducted and PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science (ISI), Embase, CINAHL databases as well as Google Scholar and Cochrane Library were systematically searched till June 2024.
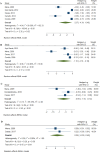
Results: 15 clinical trials (20 arms) comprising 2477 adults aged 23-80 years were included in the systematic review and 9 of them were entered in the meta-analysis. We revealed that following an enriched MED with olive oils can reduce Interleukin-6 (IL-6) (SMD: - 1.85; 95% CI: -3.69 to -0.01, I2: 99.29%) and c-reactive protein (CRP) or high-sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) (SMD: - 0.96; 95% CI: -1.49 to -0.44, I2: 91.85%); however, tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) did not improved. Moreover, a positive impact on the levels of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) and P-selectin [(SMD: -2.37; 95% CI: -4.34 to -0.40, I2: 99.38%), (SMD: -1.10; 95% CI: -2.10 to -0.10, I2: 94.96%) and (SMD: -0.65; 95% CI: -1.18 to -0.12, I2: 59.33%), respectively] were observed; however, E-selectin was unchanged.
Conclusions: The olive oils-supplemented MED demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory benefits and improvements in soluble adhesion molecules, supporting its role in reducing CVD risk. However, further studies are required to address the high heterogeneity and confirm these findings in diverse populations.
Trial registration/protocol registration: PROSPERO (CRD42023425225).
Keywords: CRP; IL-6; Inflammation; Mediterranean diet; Olive oil; sICAM-1; sVCAM-1.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical approval: No ethical approval was required as this study did not involve human participants or laboratory animals. Human ethics and consent to participate declarations: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Home/Newsroom/Fact sheets/Detail/Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). 2021 [Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

