Impact of sodium-glucose transport protein-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on the inflammasome pathway in acute myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review
- PMID: 40420176
- PMCID: PMC12105141
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-025-02777-7
Impact of sodium-glucose transport protein-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on the inflammasome pathway in acute myocardial infarction in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comprehensive review
Abstract
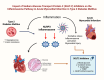
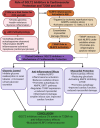
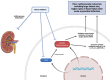
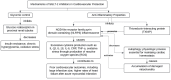
Sodium-glucose transport protein-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, initially developed for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), have emerged as potential cardioprotective agents, reducing cardiovascular mortality and improving heart failure outcomes. Recent evidence suggests that SGLT2 inhibitors exert anti-inflammatory effects, particularly through modulating the inflammasome pathway. This review explores the role of the inflammasome in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in T2DM and discusses the mechanisms by which SGLT2 inhibitors influence this pathway. We evaluate current studies on the impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on key inflammatory mediators, particularly the NLRP3 inflammasome, and discuss their potential therapeutic implications for reducing inflammation and myocardial injury in patients with T2DM experiencing AMI. In summary, the key novelties in this review lie in its focused mechanistic approach on the inflammasome pathway, its integration of diabetes and cardiovascular research, and its potential to influence future therapeutic strategies for AMI in T2DM patients. It offers a novel angle by tying together molecular mechanisms of inflammation with clinical implications in a specific patient population that faces high cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: Diabetes; Inflammation; Myocardial infarction; Sodium–glucose transport protein-2 inhibitor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lee YH, Kim SR, Bae J, Lee B, Kang ES, Ahn CW, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors suppress NLRP3 inflammasome activity via changes in ketones and insulin in type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Diabetes. 2018. 10.2337/db18-164-OR.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical