Yangke powder alleviates OVA-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 40420184
- PMCID: PMC12105270
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-025-01125-x
Yangke powder alleviates OVA-induced allergic asthma by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory airway disease that remains inadequately controlled by existing conventional treatments. A traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formula of Yangke powder (yǎng ké sǎn-YKS) has demonstrated potential in alleviating asthma symptoms and reducing its acute exacerbation. Despite clinical evidence supporting its benefit, there is still insufficient understanding of the active compounds in YKS and their underlying mechanisms, which limits its broader clinical application.
Objective: This study aims to identify the key active ingredients in YKS and explore their mechanisms, particularly through the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathways, to provide a scientific basis for its application in asthma treatment.
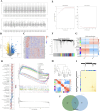
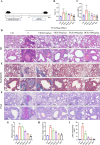
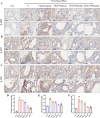
Methods: We employed UPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS to analyze YKS constituents, identified key ingredients, and explored asthma treatment mechanisms through bioinformatics, network pharmacology, Mendelian randomization, and molecular docking. The asthma model was evaluated using ovalbumin (OVA) and pulmonary function tests, while pathological examination was conducted using hematoxylin and eosin (HE), periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), and Masson trichrome stains. Concentrations of IgE, IL-4, and IL-5 were measured by ELISA, and protein and mRNA expressions were confirmed via qPCR, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot analysis.
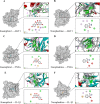
Results: A total of 174 compounds were identified in YKS by UPLC-MS, with 49 detected in the bloodstream, indicating their role as active ingredients. Bioinformatics analysis revealed 353 asthma-related targets and 972 potential targets for YKS. Key targets such as AKT1, TNF, and IL1B were validated by molecular docking. Our studies indicated that YKS modulates asthma primarily through the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB pathways, improving airway resistance, reducing inflammation, mucus production, and airway remodeling, and decreasing Th2 cytokines and IgE levels.
Conclusion: This investigation identifies Kaempferol, Norephedrine, Cynaroside, Genistein, and Rutin as critical active ingredients in YKS, impacting key biomarkers such as AKT1, TNF, and IL1B. These substances effectively modulate the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway, enhancing the management of allergic asthma.
Keywords: Asthma; Inflammation; Molecular Docking; Network Pharmacology; UPLC-Q-exactive orbitrap-MS; Yangke powder.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All animal experiments were approved by the Experimental Animal Administration Committee of Changchun University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No. 2024836) and carried out in accordance with the institutional guidelines. Consent for publication: No applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- World Health Organization. Asthma. 2023. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/asthma. Accessed 6 May 2024.
-
- Papi A, Brightling C, Pedersen SE, Reddel HK. Asthma. Lancet. 2018;391(10122):783–800. 10.1016/s0140-6736(17)33311-1. - PubMed
-
- Global initiative for asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. Global initiative for asthma. 2024. https://ginasthma.org/reports/. Accessed 22 May 2024.
Grants and funding
- YDZJ202501ZYTS697/Jilin Provincial Scientific and Technological Development Program
- YDZJ202301ZYTS136/Jilin Provincial Scientific and Technological Development Program
- YDZJ202202CXJD049/Jilin Provincial Scientific and Technological Development Program
- ZYYCXTD-D-202001/State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine of the People's Republic of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

