Research progress of CD73-adenosine signaling regulating hepatocellular carcinoma through tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 40420185
- PMCID: PMC12105175
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-025-03416-5
Research progress of CD73-adenosine signaling regulating hepatocellular carcinoma through tumor microenvironment
Abstract
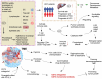
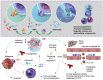
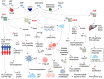
Adenosine signaling pathway is a kind of signal regulation hub widely existing in human body, which is involved in a series of physiological processes such as energy supply of body cells. CD73 is a highly concerned signaling protein in purine adenosine pathway, and its role in tumor development and prognosis has been paid more and more attention in recent years, especially in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In this paper, the specific mechanism by which CD73-adenosine signaling regulates tumor microenvironment (TME) of liver cancer tumors was analyzed in detail, highlighting the importance of this pathway as a therapeutic target to combat tumor immunosuppression and enhance the anti-tumor immune response to prevent and treat hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In addition, a variety of current targeted therapeutic strategies for adenosine metabolic pathways are summarized, including the development of new drugs in the stage of preclinical research and clinical trials, and the mechanism of action, implementation possibility, and clinical effects of these therapies are discussed. By summarizing the latest scientific research results, in this review, we attempt to paint a panorama of the mechanism of adenosine action in tumor immunotherapy, with the aim to provide a solid theoretical basis and practical guidance for subsequent research and clinical application, ultimately promoting the development of more accurate and efficient tumor immunotherapy.
Keywords: Adenosine; Adenosine receptor; CD73-adenosine signaling pathway; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors agree with the submission. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020BSZX04/Special Doctoral Fund of Hefei Hospital Affiliated to Anhui Medical University (the 2nd People's Hospital of Hefei)
- 2023AH052595/Key Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of the Province Anhui
- AHWJ2023BAc20099/Scientific Research Projects of Health Commission of Anhui Province in 2023
- 82370602/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

