Lactate and lactylation in liver diseases: energy metabolism, inflammatory immunity and tumor microenvironment
- PMID: 40421024
- PMCID: PMC12104064
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1581582
Lactate and lactylation in liver diseases: energy metabolism, inflammatory immunity and tumor microenvironment
Abstract
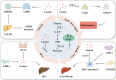
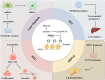
Liver diseases pose a significant threat to human health. Lactate, a byproduct of glycolysis, serves various biological functions, including acting as an energy source, a signaling molecule, and a substrate for lactylation. Lactylation is a novel lactate-dependent post-translational modification that plays a role in tumor proliferation, the regulation of immune cell function, and the modulation of gene expression. In this paper, we summarize the roles of lactate and lactylation in energy metabolism, inflammatory immunity, and the tumor microenvironment, while also elucidating recent research advancements regarding lactate and lactylation in the context of hepatic fibrosis, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Furthermore, lactate and lactylation are proposed as promising new targets for the treatment of liver diseases.
Keywords: immunology; lactate; lactylation; liver diseases; metabolism.
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Xiao, Wang, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies for lactylation in liver diseases.Life Sci. 2025 Feb 15;363:123395. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123395. Epub 2025 Jan 12. Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39809380 Review.
-
Research progress on the regulatory role of lactate and lactylation in tumor microenvironment.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025 Jul;1880(3):189339. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2025.189339. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40311713 Review.
-
Lactylation in cancer progression and drug resistance.Drug Resist Updat. 2025 Jul;81:101248. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2025.101248. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Drug Resist Updat. 2025. PMID: 40287994 Review.
-
Lactate: The Mediator of Metabolism and Immunosuppression.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 9;13:901495. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.901495. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35757394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactate and Lactylation: Dual Regulators of T-Cell-Mediated Tumor Immunity and Immunotherapy.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 21;14(12):1646. doi: 10.3390/biom14121646. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

