Inflammatory mechanisms underlying metabolic syndrome-associated and potential treatments
- PMID: 40421161
- PMCID: PMC12104644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2025.100614
Inflammatory mechanisms underlying metabolic syndrome-associated and potential treatments
Abstract
Objectives: Osteoarthritis (OA), a debilitating disease, has been recognized as a heterogenous disease, with metabolic syndrome-associated osteoarthritis (MetS-OA) emerging as a significant area of interest. Currently, the understanding of MOA remains limited, with a prevailing consensus attributing its etiology to the core components of metabolic syndrome: obesity, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. The aim of this review is to summarize the current understanding of the complex relationship between metabolic syndrome and OA from the perspectives of epidemiology and molecular biology, and to explore potential targeting strategies for metabolic syndrome in MetS-OA management.
Methods: This narrative review evaluated literature (2010-2024) from PubMed, examining clinical and mechanistic evidence linking metabolic syndrome to OA, including therapeutic studies targeting MetS-OA.
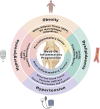
Results: Metabolic syndrome aggravate the cartilage injury in MetS-OA through metabolic biomarkers (adipokines, advanced glycation end-products and oxidized LDL), metabolic responses (oxidative stress, insulin resistance and ischemic hypoxic injuries), and abnormally activated cells (adipocytes and macrophages). It ultimately lead to the aggravation of synovitis in MetS-OA through inflammatory mediators.
Conclusions: The exploration of the relationship between metabolic syndrome and OA could benefit the development of targeting strategies for MetS-OA, including currently FDA-approved drugs for the treatment of metabolic syndrome and potential drugs targeting metabolic factors, which might provide a novel avenue for the future management of MetS-OA.
Keywords: Inflammatory mechanism; Metabolic osteoarthritis; Metabolic syndrome; Obesity.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests for any of the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An update on the association between metabolic syndrome and osteoarthritis and on the potential role of leptin in osteoarthritis.Cytokine. 2020 May;129:155043. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155043. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32078923
-
The burden of metabolic syndrome on osteoarthritic joints.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Dec 16;21(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-2081-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31842972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic syndrome meets osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012 Dec;8(12):729-37. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.135. Epub 2012 Aug 21. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22907293 Review.
-
Inter-relations between osteoarthritis and metabolic syndrome: A common link?Biochimie. 2016 Feb;121:238-52. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.12.008. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26700146 Review.
-
Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Osteoarthritis-An Updated Review.Curr Obes Rep. 2023 Sep;12(3):308-331. doi: 10.1007/s13679-023-00520-5. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Curr Obes Rep. 2023. PMID: 37578613 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Study of the Degenerative Processes of the Hip Joint Capsule and Acetabular Labrum.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 31;15(15):1932. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151932. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duong V., Oo W.M., Ding C., Culvenor A.G., Hunter D.J. Evaluation and treatment of knee pain: a review. JAMA. 2023;330:1568–1580. - PubMed
-
- Zhuo Q., Yang W., Chen J., Wang Y. Metabolic syndrome meets osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012;8:729–737. - PubMed
-
- Jansen N.E.J., Molendijk E., Schiphof D., van Meurs J.B.J., Oei E.H.G., van Middelkoop M., et al. Metabolic syndrome and the progression of knee osteoarthritis on MRI. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2023;31:647–655. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf E., Nelissen R.G., Ioan-Facsinay A., Stojanovic-Susulic V., DeGroot J., van Osch G., et al. Association between weight or body mass index and hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010;69:761–765. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

