Hydrogen sulfide as a new therapeutic target of pulmonary hypertension: an overview with update on immunomodulation
- PMID: 40421210
- PMCID: PMC12104183
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1510275
Hydrogen sulfide as a new therapeutic target of pulmonary hypertension: an overview with update on immunomodulation
Abstract
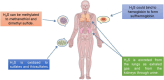
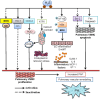
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a complex and progressive vascular disease characterized by elevated pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) and vascular resistance, leading to right ventricular failure and, ultimately, death. Current therapies primarily focus on vasodilation and symptom management, but there remains a critical need for treatments that address the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of PH. Numerous studies have identified hydrogen sulfide (H2S) as a potential therapeutic target in PH. Traditionally recognized for its toxic effects at high concentrations, H2S is now known to play crucial roles in various physiological processes, including vasodilation, anti-inflammation, and antioxidation, which are relevant to PH pathogenesis. Given its multifaceted roles in the pathophysiology of PH, H2S represents a promising therapeutic target. Strategies to enhance endogenous H2S production or administer exogenous H2S donors are being explored as potential treatments for PH. These approaches aim to harness the vasodilatory, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-remodeling properties of H2S to mitigate disease progression and improve patient outcomes. Future research should focus on optimizing H2S-based therapies and exploring their clinical efficacy and safety in PH patients.
Keywords: hydrogen sulfide; immunomodulation; organosulfur compounds; oxidative stress; pulmonary hypertension.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Zhao, Lu, Zhang, Meng, Su, Chen, Xu, Sun and Nie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Metabolism and Pulmonary Hypertension.Cells. 2021 Jun 12;10(6):1477. doi: 10.3390/cells10061477. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34204699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Hydrogen Sulfide in Development of Pulmonary Hypertension.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 1;12(6):772. doi: 10.3390/biom12060772. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling Paradigms of H2S-Induced Vasodilation: A Comprehensive Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;13(10):1158. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101158. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide and vascular regulation - An update.J Adv Res. 2020 May 16;27:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2020.05.007. eCollection 2021 Jan. J Adv Res. 2020. PMID: 33318869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) metabolism: Unraveling cellular regulation, disease implications, and therapeutic prospects for precision medicine.Nitric Oxide. 2024 Mar 1;144:20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2024.01.004. Epub 2024 Jan 17. Nitric Oxide. 2024. PMID: 38242281 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

