Status and opportunities of machine learning applications in obstructive sleep apnea: A narrative review
- PMID: 40421411
- PMCID: PMC12104685
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.04.033
Status and opportunities of machine learning applications in obstructive sleep apnea: A narrative review
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent and potentially severe sleep disorder characterized by repeated interruptions in breathing during sleep. Machine learning models have been increasingly applied in various aspects of OSA research, including diagnosis, treatment optimization, and developing biomarkers for endotypes and disease mechanisms.
Objective: This narrative review evaluates the application of machine learning in OSA research, focusing on model performance, dataset characteristics, demographic representation, and validation strategies. We aim to identify trends and gaps to guide future research and improve clinical decision-making that leverages machine learning.
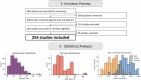
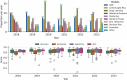
Methods: This narrative review examines data extracted from 254 scientific publications published in the PubMed database between January 2018 and March 2023. Studies were categorized by machine learning applications, models, tasks, validation metrics, data sources, and demographics.
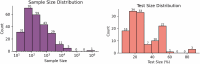
Results: Our analysis revealed that most machine learning applications focused on OSA classification and diagnosis, utilizing various data sources such as polysomnography, electrocardiogram data, and wearable devices. We also found that study cohorts were predominantly overweight males, with an underrepresentation of women, younger obese adults, individuals over 60 years old, and diverse racial groups. Many studies had small sample sizes and limited use of robust model validation.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight the need for more inclusive research approaches, starting with adequate data collection in terms of sample size and bias mitigation for better generalizability of machine learning models in OSA research. Addressing these demographic gaps and methodological opportunities is critical for ensuring more robust and equitable applications of artificial intelligence in healthcare.
Keywords: Machine Learning; Sleep Apnea.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors of the manuscript entitled “Status and Opportunities of Machine Learning Applications in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Narrative Review ” declare no competing financial or non-financial interests.
Figures



Update of
-
Status and Opportunities of Machine Learning Applications in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Narrative Review.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 10:2025.02.27.25322950. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.27.25322950. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Apr 25;28:167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.04.033. PMID: 40061337 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Status and Opportunities of Machine Learning Applications in Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Narrative Review.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 10:2025.02.27.25322950. doi: 10.1101/2025.02.27.25322950. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Apr 25;28:167-174. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.04.033. PMID: 40061337 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Polysomnography in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(13):1-38. Epub 2006 Jun 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074483 Free PMC article.
-
Achieving Better Understanding of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Treatment Effects on Cardiovascular Disease Outcomes through Machine Learning Approaches: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 29;13(5):1415. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051415. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reviewing the connection between speech and obstructive sleep apnea.Biomed Eng Online. 2016 Feb 20;15:20. doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0138-5. Biomed Eng Online. 2016. PMID: 26897500 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea: a scoping review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Apr 12. doi: 10.1007/s00405-025-09377-x. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40220178 Review.
References
-
- de Araujo Dantas A.B., Goncalves F.M., Martins A.A., et al. Worldwide prevalence and associated risk factors of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis and meta-regression. Sleep Breath. 2023;27(6):2083–2109. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
