Radioactive Tracing of Testosterone Reveals Minimal Formation of 5α-DHT in SGBS Cells and Human Primary Adipocytes
- PMID: 40421431
- PMCID: PMC12105912
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvaf087
Radioactive Tracing of Testosterone Reveals Minimal Formation of 5α-DHT in SGBS Cells and Human Primary Adipocytes
Abstract
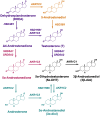
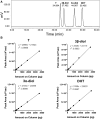
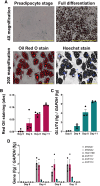
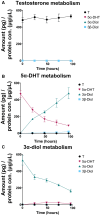
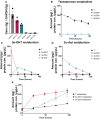
Hyperandrogenism is associated with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), acne, and alopecia. In PCOS, subcutaneous fat has been shown to contribute to hyperandrogenism through increased testosterone (T) production which is accompanied by an increase in the intra-adipose 5α-dihydrotestosterone (5α-DHT):T ratio. However, whether 5α-DHT is produced in isolated adipocytes is uncertain. Here we investigated the ability of subcutaneous human adipocytes to synthesize and inactivate 5α-DHT in a model of subcutaneous white adipocytes, Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome (SGBS) cells, and primary adipocytes. We quantified the transcripts of genes involved in the biosynthesis of 5α-DHT (AKR1C3, SRD5A1, SRD5A2, and HSD17B6) and the inactivation of 5α-DHT (AKR1C1 and AKR1C2). We found that genes that inactivate 5α-DHT were more abundantly transcribed than genes that biosynthesize 5α-DHT. This trend was reflected by radioisotope tracing. We developed a radiochromatographic method involving high-performance liquid chromatography and in-line detection of radioactive analytes with precision and accuracy within the 15% tolerance allowable by the US Food and Drug Administration criteria for analytical assays. The lower limit of detection and quantification for 5α-DHT was 3.4 pg and 15 pg, respectively. The formation of 5α-DHT was barely detectable when starting with either 10 nM T or 3α-androstanediol (3α-diol). Conversely, 5α-DHT was rapidly metabolized to 3α-diol but not 3β-diol. 3α-Diol was the major metabolite despite comparable levels of AKR1C1 and AKR1C2 transcripts. The same result was observed in both cell lines. Our data reveal that adipocytes do not biosynthesize 5α-DHT from testosterone. By contrast, 5α-DHT is rapidly metabolized by AKR1C2 in subcutaneous adipocytes.
Keywords: PCOS; adipocytes; androgen metabolism; hyperandrogenism.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Azziz R, Carmina E, Dewailly D, et al. Positions statement: criteria for defining polycystic ovary syndrome as a predominantly hyperandrogenic syndrome: an androgen excess society guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91(11):4237‐4245. - PubMed
-
- Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2(1):16057. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
