Folinic Acid Prophylaxis and Dose Adjustments Enable Safe Treatment with Pemetrexed in Patients with Renal Impairment
- PMID: 40421804
- PMCID: PMC12355014
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.3735
Folinic Acid Prophylaxis and Dose Adjustments Enable Safe Treatment with Pemetrexed in Patients with Renal Impairment
Abstract
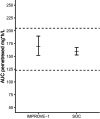
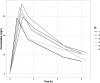
Pemetrexed is a cornerstone in chemo(immunotherapy) of non-small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma; however, it is contraindicated in patients with renal impairment due to severe toxicity concerns. Therefore, a large proportion of patients is withheld from effective chemo(immunotherapy). We performed an intra-patient 3 + 3 dose escalation renal impairment study (eGFR < 45 mL/min). The pemetrexed dose was calculated based on renal function to reach a target AUC, and patients received oral folinic acid prophylaxis 45 mg four times daily on Days 2-15 of each cycle. Endpoints included safety (incidence of hematological and non-hematological toxicity, treatment delays) and pharmacokinetics in line with regulatory guidance for renal impairment trials. Six patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) between 26 and 41 mL/min were included. All patients were successfully escalated to the full dose. Adverse event patterns and pharmacokinetics were comparable to those in patients with normal renal function. Grade I/II anemia occurred in five patients (already present at baseline). One occurrence of grade IV neutropenia was observed, which resolved without intervention. Moreover, in three patients, a 1-week treatment delay occurred. Treatment resulted in a response in four patients (n = 1 complete response, n = 2 partial response, n = 1 stable disease). Pemetrexed can be safely administered in patients with impaired renal function when the dose is calculated based on renal function and folinic acid prophylaxis is administered, thereby enabling an effective treatment modality for patients that, thus far, could not be treated.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gandhi, L. et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 378, 2078–2092 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Launay‐Vacher, V. et al. Lung cancer and renal insufficiency: prevalence and anticancer drug issues. Lung 187, 69–74 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Mita, A.C. et al. Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of pemetrexed administered every 3 weeks to advanced cancer patients with normal and impaired renal function. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 552–562 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Eli‐Lilly . Alimta – summary of product characteristics <https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product‐information/alimta‐epar‐p...>. (2009) Accessed July 24 2024.
-
- Boosman, R.J. et al. Toxicity of pemetrexed during renal impairment explained‐implications for safe treatment. Int. J. Cancer 149, 1576–1584 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

